Contents
- 1 What is an Image?
- 2 What is a Shadow?
- 3 Key Differences Between an Image and a Shadow
- 4 Difference between image and shadow in points
- 5 Conclusion
- 6 FAQs
- 6.1 What is an image?
- 6.2 What is a shadow?
- 6.3 What is the main difference between an image and a shadow?
- 6.4 How are images and shadows created?
- 6.5 Can shadows be considered as images?
- 6.6 What is the relationship between an image and a shadow?
- 6.7 How are images and shadows used in art and photography?
- 6.8 Can an object have both an image and a shadow?
- 6.9 What is the difference between a 2D image and a 3D image?
- 6.10 Can shadows exist without light?
Images and shadows are two concepts that are often used interchangeably, but they are quite different. Understanding the difference between an image and a shadow is important for a variety of reasons, including context and use, avoiding confusion, and effective communication. In this blog post, we will explore the key characteristics of an image and a shadow, and highlight the differences between the two.
What is an Image?
An image is a representation of an object or scene, usually created through a physical or digital medium. Images can be seen with the naked eye or through technological devices, such as cameras, telescopes, or microscopes. The characteristics of an image depend on the medium through which it is created.
Physical Properties of an Image
In a physical medium, an image is created through the reflection or projection of light. The resulting image can be seen directly or through a lens, such as a magnifying glass or microscope. Physical images can be two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D), and can be static or dynamic.
Digital Properties of an Image
In a digital medium, an image is created through the manipulation of binary code, or a series of 0s and 1s. Digital images can be created using software applications, such as Adobe Photoshop, or captured using digital cameras. The properties of a digital image can be manipulated through software, allowing for greater control over the final product.
Examples of Images
Examples of physical images include photographs, paintings, drawings, and sculptures. Examples of digital images include digital photographs, computer-generated graphics, and animated videos.
What is a Shadow?
A shadow is an area that is partially or completely devoid of light, created by an object blocking the path of light. The characteristics of a shadow depend on the angle and intensity of the light source, as well as the shape and size of the object blocking the light.
Physical Properties of a Shadow
In a physical medium, a shadow is created when an object blocks the path of light, casting a shadow onto a surface. The resulting shadow can be seen directly or through a lens, such as a magnifying glass or microscope. Shadows can be two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D), and can be static or dynamic.
Types of Shadows
There are different types of shadows, including umbra, penumbra, and antumbra. The umbra is the darkest part of a shadow, where all light is blocked. The penumbra is the lighter part of the shadow, where only some light is blocked. The antumbra is the area outside the shadow, where the object appears smaller than the light source.
Examples of Shadows
Examples of shadows include the shadows cast by trees, buildings, and people on a sunny day, as well as the shadows cast by objects under artificial light.
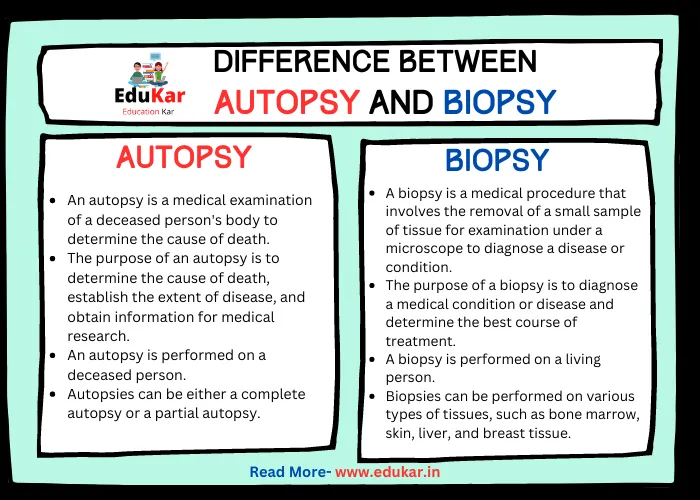
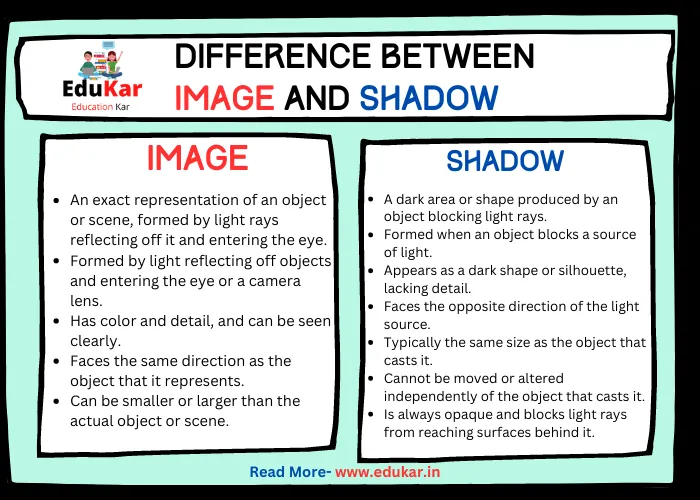
Key Differences Between an Image and a Shadow
| Difference | Image | Shadow |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An exact representation of an object or scene, formed by light rays reflecting off it and entering the eye | A dark area or shape produced by an object blocking light rays |
| Formation | Formed by light reflecting off objects and entering the eye or a camera lens | Formed when an object blocks a source of light |
| Appearance | Has color and detail, and can be seen clearly | Appears as a dark shape or silhouette, lacking detail |
| Direction | Faces the same direction as the object that it represents | Faces the opposite direction of the light source |
| Size | Can be smaller or larger than the actual object or scene | Typically the same size as the object that casts it |
| Movement | Can be moved or altered through editing or physical manipulation | Cannot be moved or altered independently of the object that casts it |
| Transparency | Can be transparent or translucent, allowing objects or scenery behind it to be seen | Is always opaque and blocks light rays from reaching surfaces behind it |
| Duration | Can persist even after the object that created it is gone | Disappears as soon as the object blocking the light source moves |
| Relationship to Object | Is directly related to the object or scene it represents | Is only indirectly related to the object that casts it |
| Usefulness | Used to capture or represent objects and scenes for a variety of purposes | Can be used artistically to create interesting compositions or effects |
Difference between image and shadow in points
- Definition:
- An image is a representation of an object or scene, created through a physical or digital medium.
- A shadow is an area that is partially or completely devoid of light, created by an object blocking the path of light.
- Characteristics:
- The characteristics of an image depend on the medium through which it is created.
- The characteristics of a shadow depend on the angle and intensity of the light source, as well as the shape and size of the object blocking the light.
- Examples:
- Examples of images include photographs, paintings, drawings, and sculptures.
- Examples of shadows include the shadows cast by objects under natural or artificial light.
- Creation:
- An image is created through the reflection or projection of light in a physical medium, or through the manipulation of binary code in a digital medium.
- A shadow is created by an object blocking the path of light.
- Types:
- Images can be two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D), and can be static or dynamic.
- Shadows can be two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D), and can be of different types such as umbra, penumbra, and antumbra.
- Context and Use:
- Images are often used in art, advertising, and scientific research to convey information or evoke emotions.
- Shadows can be used in art, photography, and design to create depth and contrast, or to highlight certain features of an object
Conclusion
Images and shadows may seem similar at first glance, they are quite different. An image is a representation of an object or scene, created through a physical or digital medium, while a shadow is an area that is partially or completely devoid of light, created by an object blocking the path of light. Understanding the difference between an image and a shadow is important for a variety of reasons, including context and use, avoiding confusion, and effective communication.
FAQs
What is an image?
An image is a representation of an object or scene created using light or other electromagnetic radiation.
What is a shadow?
A shadow is a dark area or shape created by an object blocking a source of light.
What is the main difference between an image and a shadow?
An image is a representation of an object or scene, while a shadow is the absence of light caused by an object blocking a source of light.
How are images and shadows created?
Images are created by capturing or projecting light or other electromagnetic radiation. Shadows are created when an object blocks a source of light, causing a dark area to appear behind it.
Can shadows be considered as images?
No, shadows cannot be considered as images because they do not contain any information about the object that is creating the shadow.
What is the relationship between an image and a shadow?
An image and a shadow are related in that a shadow is created by the presence of an object, which is also the subject of an image.
How are images and shadows used in art and photography?
Images and shadows are used in art and photography to create depth, contrast, and visual interest. Shadows can be used to create drama and mystery, while images can capture a moment in time or convey a particular mood or emotion.
Can an object have both an image and a shadow?
Yes, an object can have both an image and a shadow. The image is created by the object reflecting or emitting light, while the shadow is created by the object blocking a source of light.
What is the difference between a 2D image and a 3D image?
A 2D image is a flat representation of an object or scene, while a 3D image is a three-dimensional representation that appears to have depth and volume.
Can shadows exist without light?
No, shadows cannot exist without light. Shadows are created by the absence of light caused by an object blocking a source of light.