Contents
- 1 Introduction
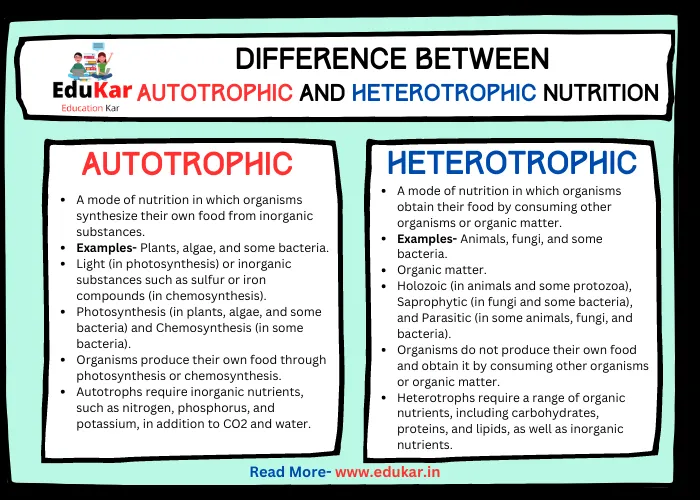
- 2 What does it mean to be healthy?
- 3 What does it mean to be disease-free?
- 4 Differences between Healthy and Disease Free
- 5 The importance of striving for both health and disease-free status
- 6 The role of preventive medicine in achieving both health and disease-free status
- 7 Benefits of preventive medicine include:
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 Important FAQs:
- 9.1 What does it mean to be healthy?
- 9.2 What does it mean to be disease-free?
- 9.3 What is the difference between being healthy and being disease-free?
- 9.4 Why is it important to strive for both health and disease-free status?
- 9.5 What role does preventive medicine play in achieving both health and disease-free status?
- 9.6 Can a person be healthy without being disease-free?
- 9.7 Can a person be disease-free without being healthy?
This blog explores the difference between being healthy and being disease-free, two concepts that are often confused. We delve into the factors that contribute to overall health and being disease-free, and why striving for both is important. Additionally, we discuss the role of preventive medicine in achieving both health and disease-free status.
Introduction
Maintaining good health is essential for living a happy, productive life. However, many people confuse being healthy with being disease-free. While the two are closely related, there are some key differences between the two concepts that are worth exploring.
What does it mean to be healthy?
Being healthy means more than just the absence of disease or illness. Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity. A healthy person is someone who is physically fit, mentally alert, and socially engaged. They have a positive outlook on life and enjoy a high level of overall well-being.
Factors that contribute to overall health include:
- A balanced diet that includes all essential nutrients.
- Regular physical activity that promotes cardiovascular health, builds muscle strength and endurance, and improves flexibility and balance.
- Adequate sleep and rest.
- Stress management techniques such as mindfulness meditation or yoga.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor and manage any health issues.
What does it mean to be disease-free?
Being disease-free means that a person is free from any infectious or non-infectious disease or condition that can negatively affect their physical or mental health. Disease-free people have a lower risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or cancer.
Factors that contribute to being disease-free include:
- Regular preventive healthcare, such as vaccinations and cancer screenings.
- Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding unhealthy habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug abuse.
- Practicing good hygiene to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
- Avoiding exposure to environmental toxins.
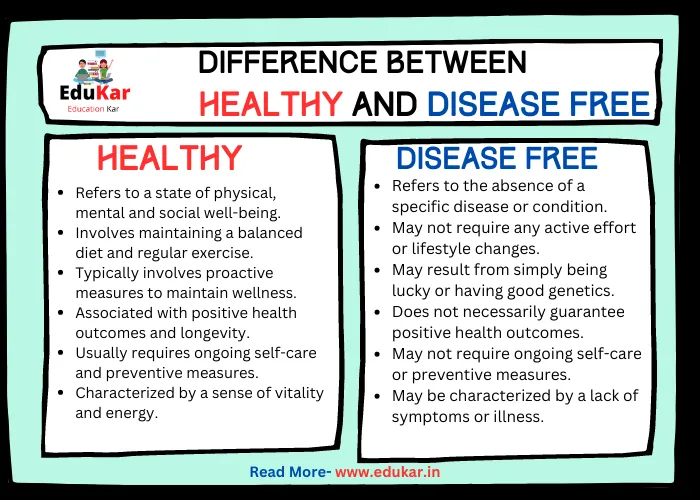
Differences between Healthy and Disease Free
| S.No. | Healthy | Disease-Free |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Refers to a state of physical, mental and social well-being | Refers to the absence of a specific disease or condition |
| 2 | Involves maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise | May not require any active effort or lifestyle changes |
| 3 | Typically involves proactive measures to maintain wellness | May result from simply being lucky or having good genetics |
| 4 | Associated with positive health outcomes and longevity | Does not necessarily guarantee positive health outcomes |
| 5 | Usually requires ongoing self-care and preventive measures | May not require ongoing self-care or preventive measures |
| 6 | Characterized by a sense of vitality and energy | May be characterized by a lack of symptoms or illness |
| 7 | Can contribute to a higher quality of life | May not necessarily have a significant impact on quality of life |
| 8 | May involve regular check-ups and health screenings | May not require regular check-ups or health screenings |
| 9 | Can involve a proactive approach to managing one’s health | May not require any management or treatment |
| 10 | Can be achieved and maintained through a variety of lifestyle factors | Can be achieved by simply not having a specific disease or condition |
The importance of striving for both health and disease-free status
Both health and disease-free status are essential for leading a happy, productive life. Striving for both can help reduce the risk of developing chronic conditions and improve overall well-being. For example, a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity and a balanced diet can help prevent obesity, which is a significant risk factor for many chronic diseases. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help catch any health issues early, when they are most treatable.
The role of preventive medicine in achieving both health and disease-free status
Preventive medicine is an essential component of achieving both health and disease-free status. Preventive medicine focuses on identifying and addressing risk factors for disease before they become problematic. This can include measures such as vaccinations, cancer screenings, and lifestyle modifications.
Benefits of preventive medicine include:
- Reduced healthcare costs over the long term.
- Improved quality of life.
- Reduced morbidity and mortality from preventable diseases.
- Increased productivity and engagement in daily life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while being healthy and disease-free are closely related, there are some important differences between the two. Striving for both can help reduce the risk of developing chronic conditions and improve overall well-being. Preventive medicine is an essential component of achieving both health and disease-free status and can provide many benefits over the long term. By prioritizing both health and disease-free status, we can live happier, healthier lives.
Important FAQs:
What does it mean to be healthy?
Being healthy means having a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, not just the absence of disease or infirmity. It encompasses a positive outlook on life, a balanced diet, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and rest, and stress management techniques.
What does it mean to be disease-free?
Being disease-free means that a person is free from any infectious or non-infectious disease or condition that can negatively affect their physical or mental health. This can be achieved through regular preventive healthcare, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and avoiding exposure to environmental toxins.
What is the difference between being healthy and being disease-free?
Being healthy refers to overall physical, mental, and social well-being, while being disease-free means being free from any infectious or non-infectious disease or condition. A person may be healthy but still have a chronic condition, while a disease-free person may still struggle with mental health issues.
Why is it important to strive for both health and disease-free status?
Striving for both health and disease-free status can help reduce the risk of developing chronic conditions, improve overall well-being, and increase productivity and engagement in daily life.
What role does preventive medicine play in achieving both health and disease-free status?
Preventive medicine is essential in identifying and addressing risk factors for disease before they become problematic. This includes measures such as vaccinations, cancer screenings, and lifestyle modifications.
Can a person be healthy without being disease-free?
Yes, a person can be healthy without being disease-free. For example, a person may have a chronic condition such as diabetes or hypertension but still maintain an overall healthy lifestyle.
Can a person be disease-free without being healthy?
Yes, a person can be disease-free without being healthy. For example, a person may not have any infectious or non-infectious diseases, but they may still struggle with mental health issues.