Contents
Learn about the key differences between these two types of salts, including their chemical compositions, formation processes, and practical applications. Read on to gain a deeper understanding of these important chemical compounds.
Introduction
Salts are ionic compounds made up of positively charged ions, known as cations, and negatively charged ions, known as anions. Salts play an important role in various fields, such as chemistry, biology, and medicine. There are different types of salts, including double salts and complex salts.
Double Salts
Double salts are salts that are formed by the combination of two different salts. Double salts have a distinct chemical formula, and the ions in the double salt are held together by ionic bonds. The formation of double salts occurs when two different salts combine in solution, and they crystallize together.
For example, the double salt KAl(SO4)2·12H2O is formed by the combination of potassium sulfate and aluminum sulfate.
Double salts are known for their unique properties. They have a different crystal structure than the original salts, and their solubility in water is different. Double salts can also be used for various applications, such as in the production of fertilizers and dyes.
Also Read: Difference Between Conventional and Non-Conventional Source of Energy
Complex Salts
Complex salts are formed by the combination of a metal ion and a ligand. Ligands are molecules or ions that have a lone pair of electrons, which can bond with the metal ion. Complex salts have a different chemical formula than the original metal ion and ligand, and they are held together by covalent bonds. The formation of complex salts occurs when the metal ion and the ligand combine in solution.
Complex salts have different properties than the metal ion or the ligand alone. They have a different color, solubility, and reactivity. Complex salts are commonly used in various fields, such as in the production of catalysts, pigments, and drugs.
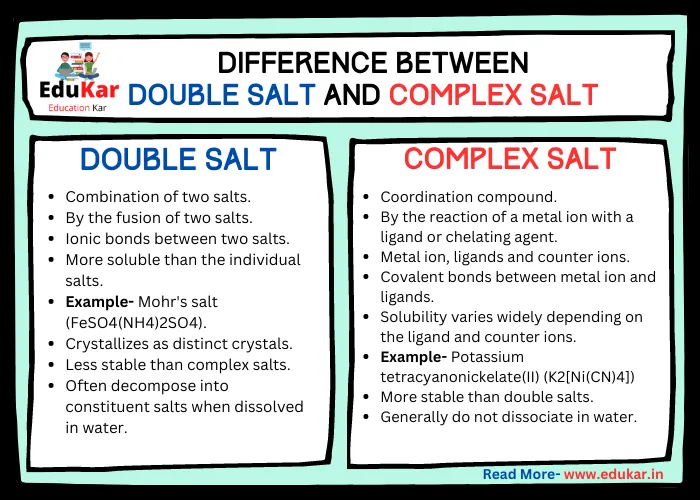
Differences between Double Salts and Complex Salts
| Feature | Double Salt | Complex Salt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of two salts | Coordination compound |
| Formation | By the fusion of two salts | By the reaction of a metal ion with a ligand or chelating agent |
| Chemical formula | AB·CD | [M(A)(B)(C)] |
| Composition | Two distinct salts | Metal ion, ligands and counter ions |
| Bonding | Ionic bonds between two salts | Covalent bonds between metal ion and ligands |
| Solubility | More soluble than the individual salts | Solubility varies widely depending on the ligand and counter ions |
| Examples | Mohr’s salt (FeSO4(NH4)2SO4) | Potassium tetracyanonickelate(II) (K2[Ni(CN)4]) |
| Crystal structure | Crystallizes as distinct crystals | Complex 3D structure with the metal ion at the center |
| Stability | Less stable than complex salts | More stable than double salts |
| Reaction with water | Often decompose into constituent salts when dissolved in water | Generally do not dissociate in water |
| Use | As a laboratory reagent or fertilizer | As a catalyst or in pharmaceuticals |
Summary
Double salts and complex salts are two different types of salts that have unique properties, formation, and uses.
Double salts are formed by the combination of two different salts, while complex salts are formed by the combination of a metal ion and a ligand. Double salts have a different crystal structure and solubility than the original salts, while complex salts have a different color, solubility, and reactivity than the metal ion or the ligand alone.
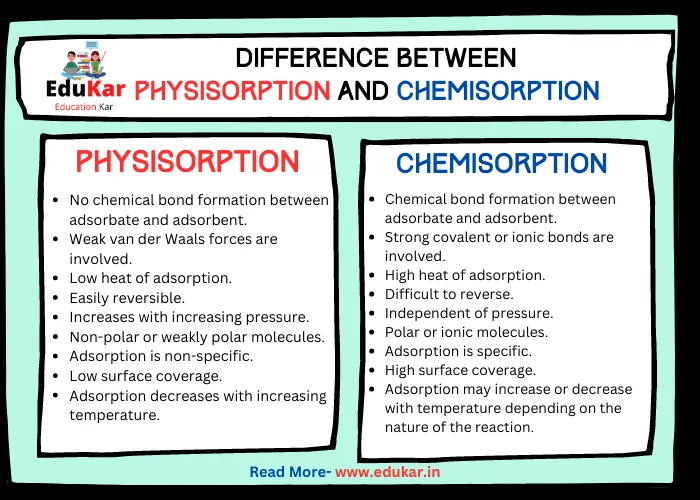
Also Read: Difference Between Physisorption and Chemisorption
Understanding the difference between double salts and complex salts is important in various fields, such as chemistry, biology, and medicine. Future research and applications for double salts and complex salts will continue to expand our understanding of these important compounds.
FAQs
What is a double salt?
A double salt is a combination of two or more salts that crystallize together in a definite ratio, resulting in a distinct compound with unique physical and chemical properties.
What is a complex salt?
A complex salt is a salt that contains a central metal ion or cation, surrounded by a group of ligands or anions that are coordinated to it in a specific way, resulting in a stable structure.
How do double salts differ from complex salts?
Double salts are a combination of two or more simple salts, while complex salts contain a central metal ion or cation and coordinating ligands or anions.
What are the physical and chemical properties of double salts?
Double salts have unique physical and chemical properties that differ from their constituent simple salts. For example, they may have a different crystal structure, solubility, or color. Double salts may also exhibit different chemical reactivity or behavior than their constituent salts.
What are the physical and chemical properties of complex salts?
Complex salts also have unique physical and chemical properties due to their specific coordination geometry and ligand interactions with the central metal ion. These properties can include different color, solubility, and reactivity than their constituent ions or ligands. Additionally, complex salts can have important applications in areas such as catalysis, electronics, and materials science.
How are double salts and complex salts used?
Double salts and complex salts have a variety of uses in industrial, agricultural, and scientific applications. For example, alum is used in water treatment to remove impurities, while potassium hexacyanoferrate (II) is used as a blue pigment in paints and dyes. Complex salts have important uses in catalysis, such as in the Haber-Bosch process for producing ammonia, and in electronics, such as in the production of LEDs.