Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What are diamond and graphite?
- 3 Differences between Diamond and Graphite
- 4 Similarities between diamond and graphite
- 5 Applications of diamond and graphite:
- 6 Summary
- 7 FAQs
- 7.1 What is the difference between diamond and graphite?
- 7.2 What is the atomic structure of diamond and graphite?
- 7.3 What are the physical properties of diamond and graphite?
- 7.4 What are the uses of diamond and graphite?
- 7.5 How do diamond and graphite form?
- 7.6 Are diamond and graphite the only allotropes of carbon?
Learn about the fundamental differences between diamond and graphite – two of the most well-known allotropes of carbon in this informative article by Edukar. Discover the unique properties, structures, and applications of these materials and gain a deeper understanding of their contrasting characteristics.
Introduction
Diamond and graphite are two of the most well-known forms of carbon in the world. They both have unique properties and uses that make them important in various industries. Understanding the differences between diamond and graphite is essential for many fields, including material science, chemistry, and engineering.
What are diamond and graphite?
Diamond is a form of carbon that has a unique crystal structure. Each carbon atom in a diamond is bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement, making it one of the hardest materials on earth. Diamond has a very high melting point, which makes it useful in high-temperature applications. It is also transparent and has a high refractive index, which makes it ideal for use in jewelry.
Also Read: Difference Between Mineral and Ore
Graphite, on the other hand, is a soft, black, and lustrous mineral that is also composed of carbon. Graphite is made up of layers of hexagonal carbon atoms that are bonded to each other. The layers can slide over one another, making graphite soft and slippery. Graphite has a relatively low melting point and is a good conductor of electricity, making it useful in applications such as batteries and electrodes.
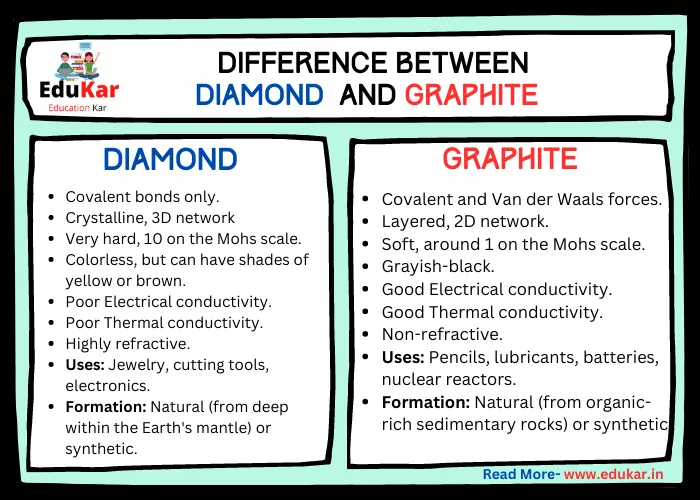
Differences between Diamond and Graphite
| Properties | Diamond | Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C | C |
| Bonding | Covalent bonds only | Covalent and Van der Waals forces |
| Structure | Crystalline, 3D network | Layered, 2D network |
| Hardness | Very hard, 10 on the Mohs scale | Soft, around 1 on the Mohs scale |
| Color | Colorless, but can have shades of yellow or brown | Grayish-black |
| Electrical conductivity | Poor | Good |
| Thermal conductivity | Poor | Good |
| Optical properties | Highly refractive | Non-refractive |
| Uses | Jewelry, cutting tools, electronics | Pencils, lubricants, batteries, nuclear reactors |
| Formation | Natural (from deep within the Earth’s mantle) or synthetic | Natural (from organic-rich sedimentary rocks) or synthetic |
Similarities between diamond and graphite
Despite their differences, diamond and graphite also have some similarities. They are both made up of carbon atoms and are allotropes of carbon. They are both formed under high pressure and temperature conditions and have unique properties that make them useful in different applications.
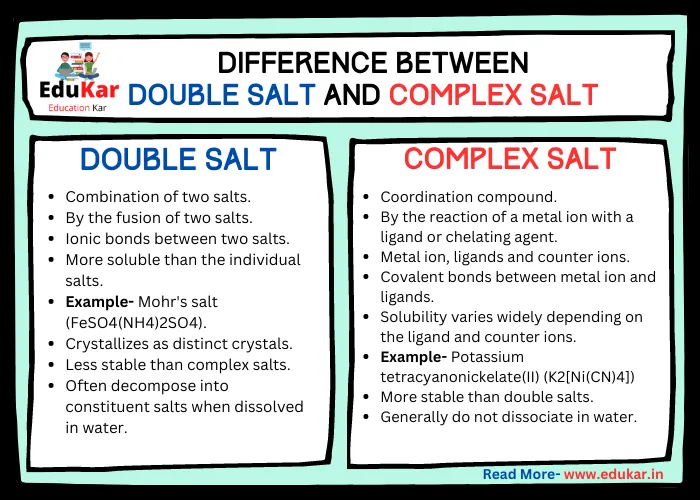
Also Read: Difference Between Double Salt and Complex Salt
Applications of diamond and graphite:
The properties of diamond and graphite make them useful in various industries.
Diamond is used in the production of cutting tools, grinding wheels, and polishing pads for the semiconductor industry. It is also used in high-pressure experiments, high-temperature applications, and as a coating for medical implants.
Graphite is used in the production of electrodes for batteries, electrical contacts, and lubricants. It is also used in the manufacture of brake linings, gaskets, and insulation for high-temperature applications.
In addition to these industrial uses, both diamond and graphite have potential applications in biomedicine. Diamond has been used in drug delivery systems, and its biocompatibility makes it a promising material for implants and prostheses. Graphite has been studied for use in biomedical imaging, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Summary
Diamond and graphite are two unique forms of carbon with distinct properties and uses. Diamond’s hardness, transparency, and refractive index make it ideal for use in jewelry and high-temperature applications. Graphite’s conductivity, lubricity, and low friction make it useful in electrical and industrial applications. Understanding the differences between diamond and graphite is essential for scientists and engineers who work with these materials. As research continues, new and exciting applications for diamond and graphite will continue to emerge.
Also Read: Difference Between Conventional and Non-Conventional Source of Energy
FAQs
What is the difference between diamond and graphite?
Diamond and graphite are two allotropes of carbon. The main difference between them lies in their atomic structure, physical properties, and uses.
What is the atomic structure of diamond and graphite?
Diamond has a tetrahedral crystal structure where each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms in a three-dimensional arrangement. Graphite has a layered structure, where each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms in a planar hexagonal arrangement.
What are the physical properties of diamond and graphite?
Diamond is the hardest known material and has a high melting point of about 3,500°C. Graphite is a soft and slippery material and has a much lower melting point of about 3,600°C.
What are the uses of diamond and graphite?
Diamond is used in jewelry, cutting and drilling tools, and electronic devices due to its hardness and excellent thermal conductivity. Graphite is used in lubricants, pencils, batteries, and as a moderator in nuclear reactors due to its softness, electrical conductivity, and high melting point.
How do diamond and graphite form?
Diamond forms under high pressure and temperature conditions deep within the Earth’s mantle. Graphite forms from the decomposition of organic matter over millions of years under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Are diamond and graphite the only allotropes of carbon?
No, there are several other allotropes of carbon, such as fullerenes, carbon nanotubes, and amorphous carbon.