Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Autopsy
- 3 Biopsy
- 4 Differences between Autopsy and Biopsy
- 5 Conclusion
- 6 Important FAQs
- 6.1 What is an autopsy?
- 6.2 What is a biopsy?
- 6.3 What are the main differences between autopsy and biopsy?
- 6.4 What is the purpose of an autopsy?
- 6.5 What is the purpose of a biopsy?
- 6.6 Are there any risks associated with autopsy and biopsy?
- 6.7 Which procedure is more invasive, autopsy or biopsy?
- 6.8 Can autopsy and biopsy be used together to diagnose a medical condition?
Learn about the key differences between autopsy and biopsy in our detailed blog post. Understand the purposes, procedures, and risks associated with both procedures to make informed decisions about your medical care.
Introduction
When it comes to medical procedures, it’s important to know the differences between different types of tests and treatments. Two medical procedures that are often confused with each other are autopsy and biopsy. Although they both involve the examination of tissues, organs or cells, they are very different procedures with different purposes and methods.
Autopsy
Autopsy, also known as a post-mortem examination, is an examination of a body after death. The word “autopsy” comes from the Greek words “auto” meaning “self” and “opsis” meaning “to see.” An autopsy is performed by a pathologist, who is a medical doctor trained in the study of diseases and the causes of death. The purpose of an autopsy is to determine the cause of death and to investigate any diseases or injuries that the deceased may have had.
When an autopsy is performed?
An autopsy is usually performed when the cause of death is unknown or when there is suspicion of foul play. It may also be performed to provide closure for the family or to improve medical knowledge. However, it is important to note that an autopsy cannot be performed without the consent of the deceased’s family or next of kin.
How an autopsy is performed?
The procedure for an autopsy can vary depending on the circumstances of the death and the organs or tissues that need to be examined. Generally, an autopsy involves a thorough examination of the body, including the external features, such as the head, hands, and feet, as well as the internal organs, such as the heart, lungs, liver, and brain. During the examination, the pathologist will take samples of tissues or fluids from different parts of the body to be examined under a microscope.
Types of autopsy
There are two main types of autopsies: complete and partial. A complete autopsy involves a thorough examination of the entire body, including all organs and tissues, while a partial autopsy only examines specific parts of the body, such as the brain or heart.
Benefits and Risks of an autopsy
One of the benefits of an autopsy is that it can provide valuable information about the cause of death, which can be helpful for families who may be concerned about genetic diseases or medical conditions. Additionally, an autopsy can provide valuable medical knowledge, which can help in the development of new treatments and therapies for diseases.
However, there are also some risks associated with an autopsy, such as infection and damage to the body. Additionally, some families may find the procedure emotionally distressing and may not want to consent to an autopsy.
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of tissue or cells is taken from the body for examination. The word “biopsy” comes from the Greek words “bio” meaning “life” and “opsis” meaning “to see.” A biopsy can be performed on any part of the body, including the skin, organs, and bones. Biopsies can be performed using a variety of methods, including needle biopsy, incisional biopsy, and excisional biopsy.
When a biopsy is performed?
A biopsy is usually performed when there is suspicion of a medical condition, such as cancer. Biopsies are also used to diagnose other medical conditions, such as infections and inflammatory disorders. Biopsies can also be used to monitor the progress of a medical condition and to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments.
How a biopsy is performed?
The procedure for a biopsy can vary depending on the type of biopsy being performed and the part of the body being examined. In a needle biopsy, a thin needle is inserted into the tissue to collect a small sample. In an incisional biopsy, a small incision is made in the skin to remove a sample of tissue. In an excisional biopsy, the entire lump or abnormal tissue is removed.
Benefits and Risks of biopsy
One of the benefits of a biopsy is that it can provide a definitive diagnosis, which can help in the development of an appropriate treatment plan. Biopsies can also provide valuable information about the stage and severity of a medical condition, which can help in determining the prognosis.
However, there are also some risks associated with a biopsy, such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues. Additionally, some patients may experience pain or discomfort during the procedure.
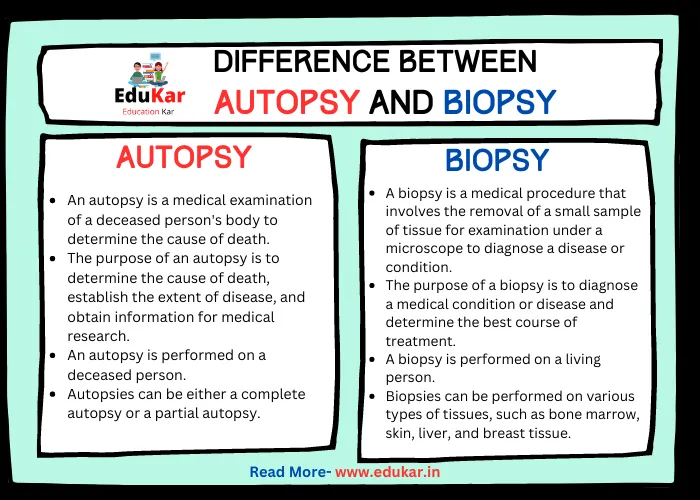
Differences between Autopsy and Biopsy
| Difference | Autopsy | Biopsy |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | An autopsy is a medical examination of a deceased person’s body to determine the cause of death. | A biopsy is a medical procedure that involves the removal of a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope to diagnose a disease or condition. |
| Purpose | The purpose of an autopsy is to determine the cause of death, establish the extent of disease, and obtain information for medical research. | The purpose of a biopsy is to diagnose a medical condition or disease and determine the best course of treatment. |
| Patient Status | An autopsy is performed on a deceased person. | A biopsy is performed on a living person. |
| Types | Autopsies can be either a complete autopsy or a partial autopsy. | Biopsies can be performed on various types of tissues, such as bone marrow, skin, liver, and breast tissue. |
| Procedure | An autopsy involves a full-body examination, including external and internal examination, and may include X-rays, blood tests, and other laboratory tests. | A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue using a needle or surgical procedure, which is then examined under a microscope. |
| Time | An autopsy is performed after a person has died. | A biopsy is usually performed when a person is alive, although a biopsy can be performed after death in certain cases. |
| Risks | Autopsies do not pose any risks to the deceased person. | Biopsies can have risks, such as bleeding, infection, and damage to nearby organs. |
| Consent | Autopsies require consent from the deceased person’s family or legal representative. | Biopsies require consent from the patient or the patient’s legal representative. |
| Results | Autopsy results are usually available within a few weeks. | Biopsy results are usually available within a few days. |
| Costs | Autopsies are typically covered by insurance or paid for by the hospital or medical examiner’s office. | Biopsies may or may not be covered by insurance, and the cost can vary depending on the type of biopsy and where it is performed. |
Conclusion
While autopsy and biopsy may seem similar at first glance, they are very different procedures with different purposes and methods. Autopsy is performed after death to determine the cause of death and investigate any diseases or injuries, while biopsy is performed on a living person to diagnose and monitor medical conditions. Both procedures have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, and it is important for patients and families to understand these differences in order to make informed decisions about their medical care.
Important FAQs
What is an autopsy?
An autopsy is a post-mortem examination of a body to determine the cause of death and investigate any diseases or injuries that the deceased may have had.
What is a biopsy?
A biopsy is a medical procedure that involves the removal of a small sample of tissue from the body for diagnostic purposes.
What are the main differences between autopsy and biopsy?
Autopsy is performed after death, while biopsy is performed on a living person. Autopsy is used to determine the cause of death and investigate any diseases or injuries, while biopsy is used to diagnose and monitor medical conditions.
What is the purpose of an autopsy?
The primary purpose of an autopsy is to determine the cause of death and investigate any diseases or injuries that the deceased may have had. Autopsy can also provide valuable medical knowledge and closure for families.
What is the purpose of a biopsy?
The purpose of a biopsy is to diagnose and monitor medical conditions. Biopsy can also provide valuable information about the stage and severity of a medical condition, which can help in determining the prognosis.
Are there any risks associated with autopsy and biopsy?
Yes, there are risks associated with both procedures. Autopsy can be emotionally distressing for families and carries some risks of infection and damage to the body. Biopsy carries some risks of bleeding, infection, and pain.
Which procedure is more invasive, autopsy or biopsy?
Autopsy is more invasive than biopsy, as it involves a thorough examination of the entire body, while biopsy only involves the removal of a small sample of tissue.
Can autopsy and biopsy be used together to diagnose a medical condition?
Yes, autopsy and biopsy can be used together to diagnose and monitor medical conditions. Autopsy can provide valuable information about the progression and severity of a medical condition, while biopsy can provide a definitive diagnosis and guide treatment decisions.