Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is Clay Soil?
- 3 What is Sandy Soil?
- 4 Differences between Clay Soil and Sandy Soil
- 5 Improving Clay and Sandy Soils
- 6 Summary
- 7 FAQs
- 7.1 What is clay soil?
- 7.2 What is sandy soil?
- 7.3 What are the main differences between clay soil and sandy soil?
- 7.4 How does the texture of clay soil differ from sandy soil?
- 7.5 Which soil type has a higher water-holding capacity?
- 7.6 Which soil type has better drainage?
- 7.7 Which soil type has a higher nutrient content?
- 7.8 Which soil type is better for growing vegetables?
- 7.9 Which soil type is better for growing succulents?
- 7.10 How can I tell if my soil is clay or sandy?
This article by Edukar explains the key differences between clay soil and sandy soil, including their composition, water-holding capacity, drainage, and suitability for various plants. Whether you’re a gardener, landscaper, or simply curious about soil types, this informative guide will help you understand the unique properties of these two common types of soil.
Introduction
Soil is a vital component for plants to grow and thrive. It serves as the foundation for plant roots to anchor and absorb nutrients and water. Different types of soil have unique properties that affect plant growth.
What is Clay Soil?
Clay soil is a soil type that has a high percentage of clay particles. It is made up of very fine particles that have a smooth texture when dry, but sticky and heavy when wet. Some of its properties include:
Texture and Composition
Clay soil is dense and compact, which makes it challenging to work with. It has a high water-holding capacity, which means it can hold onto water for extended periods, making it difficult for plant roots to absorb nutrients.
Characteristics
Clay soil has high nutrient retention capacity, making it fertile. However, it drains water slowly, which can cause waterlogging and root rot. Additionally, it can become hard and difficult to penetrate when it dries out.
Also Read: Difference Between Rabi and Kharif Crops
What is Sandy Soil?
Sandy soil is another common soil type that has a high percentage of sand particles. It is gritty and coarse to the touch and tends to drain water quickly. Some of its properties include:
Texture and Composition
Sandy soil has a loose and porous texture, which makes it easy to work with. It is composed of larger particles, allowing for more air circulation and drainage.
Characteristics
Sandy soil has a low water-holding capacity, which makes it challenging for plants to retain water and nutrients. However, it drains water quickly, which can prevent waterlogging and root rot. Additionally, it has a low nutrient retention capacity, which means it requires frequent fertilization.
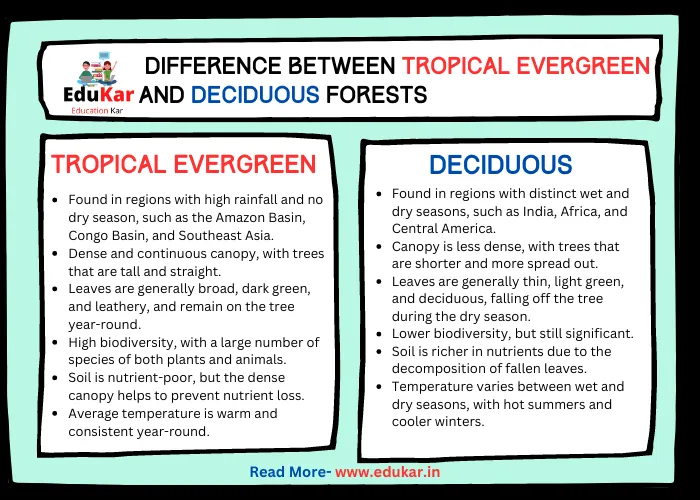
Also Read: Difference Between Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forest
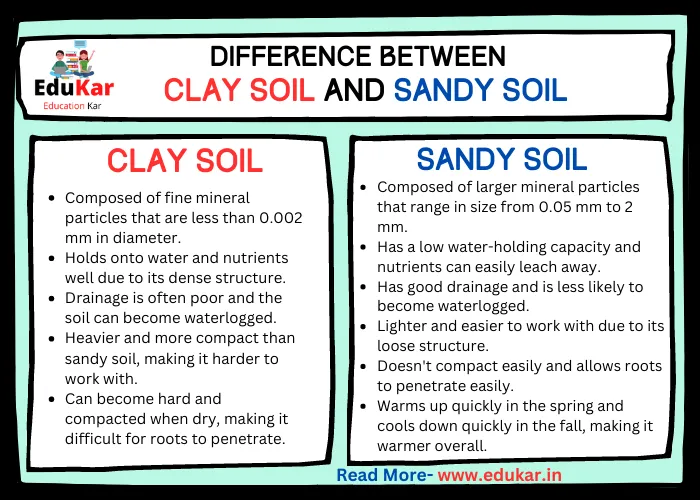
Differences between Clay Soil and Sandy Soil
| S.No. | Clay Soil | Sandy Soil |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Composed of fine mineral particles that are less than 0.002 mm in diameter. | Composed of larger mineral particles that range in size from 0.05 mm to 2 mm. |
| 2 | Holds onto water and nutrients well due to its dense structure. | Has a low water-holding capacity and nutrients can easily leach away. |
| 3 | Drainage is often poor and the soil can become waterlogged. | Has good drainage and is less likely to become waterlogged. |
| 4 | Heavier and more compact than sandy soil, making it harder to work with. | Lighter and easier to work with due to its loose structure. |
| 5 | Can become hard and compacted when dry, making it difficult for roots to penetrate. | Doesn’t compact easily and allows roots to penetrate easily. |
| 6 | Warms up more slowly in the spring and retains heat longer in the fall, making it cooler overall. | Warms up quickly in the spring and cools down quickly in the fall, making it warmer overall. |
| 7 | Often has a high pH and can be alkaline, which may limit the types of plants that can grow well in it. | Has a low pH and can be acidic, which may also limit the types of plants that can grow well in it. |
| 8 | Can be sticky and difficult to work with when wet. | Doesn’t stick together and is easy to work with even when wet. |
| 9 | Can be prone to erosion due to its dense structure and poor drainage. | Is less prone to erosion due to its loose structure and good drainage. |
Improving Clay and Sandy Soils
Improving the soil structure and fertility is essential to optimize plant growth in clay and sandy soils. Here are some tips to improve each soil type:
Improving Clay Soil
- Add organic matter such as compost, leaf litter, or manure to increase the soil’s fertility.
- Use gypsum or lime to break down the clay particles, making it easier for plant roots to penetrate.
- Avoid over-watering, which can lead to waterlogging and root rot.
Improving Sandy Soil
- Add organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve the soil’s nutrient retention capacity.
- Use mulch to retain moisture in the soil and prevent it from drying out too quickly.
- Fertilize regularly to compensate for the low nutrient retention capacity.
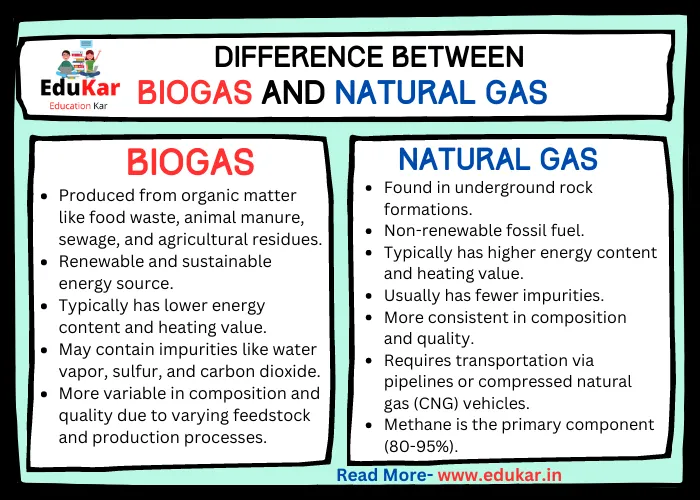
Also Read: Difference Between Biogas and Natural Gas
Summary
Understanding the differences between clay soil and sandy soil is crucial for successful gardening or farming. Each soil type has unique characteristics that can either benefit or hinder plant growth. By taking the time to understand the unique properties of each soil type and implementing strategies to improve soil structure and fertility, gardeners and farmers can optimize plant growth and yield.
FAQs
What is clay soil?
Clay soil is a soil type that contains a high percentage of clay particles. It is typically heavy and dense, and has a high water-holding capacity.
What is sandy soil?
Sandy soil is a soil type that contains a high percentage of sand particles. It is typically light and porous, and has a low water-holding capacity.
What are the main differences between clay soil and sandy soil?
The main differences between clay soil and sandy soil are their texture, water-holding capacity, drainage, nutrient content, and suitability for growing different types of plants.
How does the texture of clay soil differ from sandy soil?
Clay soil is heavy and dense, while sandy soil is light and porous.
Which soil type has a higher water-holding capacity?
Clay soil has a higher water-holding capacity than sandy soil.
Which soil type has better drainage?
Sandy soil has better drainage than clay soil.
Which soil type has a higher nutrient content?
Clay soil has a higher nutrient content than sandy soil.
Which soil type is better for growing vegetables?
Clay soil is generally better for growing vegetables, as it has a higher nutrient content and better water-holding capacity.
Which soil type is better for growing succulents?
Sandy soil is generally better for growing succulents, as it has better drainage and a lower water-holding capacity.
How can I tell if my soil is clay or sandy?
One way to tell if your soil is clay or sandy is to squeeze a handful of it. If it forms a sticky ball that holds its shape, it is likely clay soil. If it falls apart easily, it is likely sandy soil. Another way is to observe the texture and color of the soil: clay soil is usually dark and heavy, while sandy soil is usually light and grainy.