Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Cabinet of Ministers
- 3 Council of Ministers
- 4 Differences between the Cabinet and Council of Ministers
- 5 Importance of understanding the difference
- 6 Summary
- 7 FAQs
- 7.1 What is the Cabinet?
- 7.2 What is the Council of Ministers?
- 7.3 What is the main difference between the Cabinet and Council of Ministers?
- 7.4 Who is typically a part of the Cabinet?
- 7.5 Who is typically a part of the Council of Ministers?
- 7.6 What are the responsibilities of the Cabinet and Council of Ministers?
- 7.7 Can the Cabinet and Council of Ministers have overlapping responsibilities?
- 7.8 Can the Cabinet and Council of Ministers be dissolved or restructured?
This article by Edukar discusses the key differences between Cabinet and Council of Ministers in a government. It explains the roles and responsibilities of each group and highlights the differences that set them apart. Whether you’re a student of political science or just curious about government structures, this informative article will provide valuable insights into the workings of a government.
Introduction
The Cabinet and Council of Ministers are two important bodies of the Indian government that play a crucial role in the country’s governance and decision-making process. It is important to understand the difference between these two bodies as it affects the functioning of the government.
Cabinet of Ministers
The Cabinet of Ministers is a smaller and more powerful body that consists of the Prime Minister and senior ministers. It is responsible for taking key decisions related to national security, foreign affairs, finance, and other important issues.
Also See: Difference Between Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat
Role and powers of the Cabinet: The Cabinet has the power to make decisions on behalf of the government, and its decisions are binding on all other government departments.
Examples of Cabinet decisions: Some examples of Cabinet decisions include the approval of the annual budget, appointment of key officials, and approval of major policy decisions. The Cabinet is also responsible for the overall management of the government and ensuring that the government functions efficiently.
Council of Ministers
The Council of Ministers is a larger body that consists of all the ministers in the government, including the Prime Minister. Its role is advisory in nature, and it is responsible for providing guidance and support to the Cabinet. The Council of Ministers meets regularly to discuss and review government policies and programs.
Role and powers of the Council: The Council of Ministers has the power to make recommendations to the Cabinet on important issues, but its decisions are not binding. The Council of Ministers is responsible for implementing government policies and programs at the grassroots level.
Also See: Difference Between State and Government
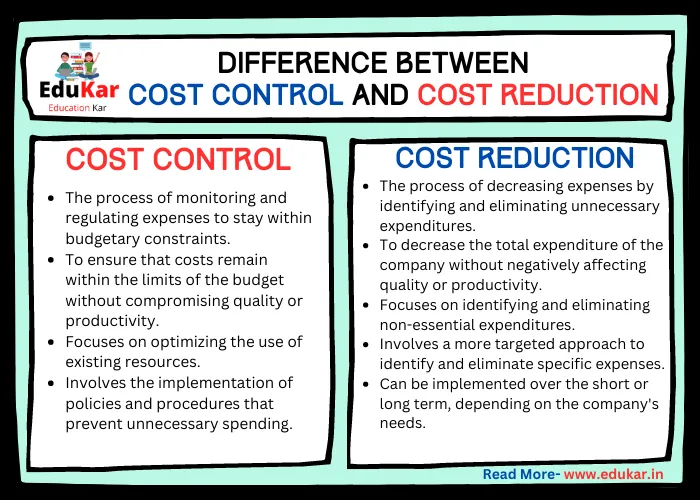
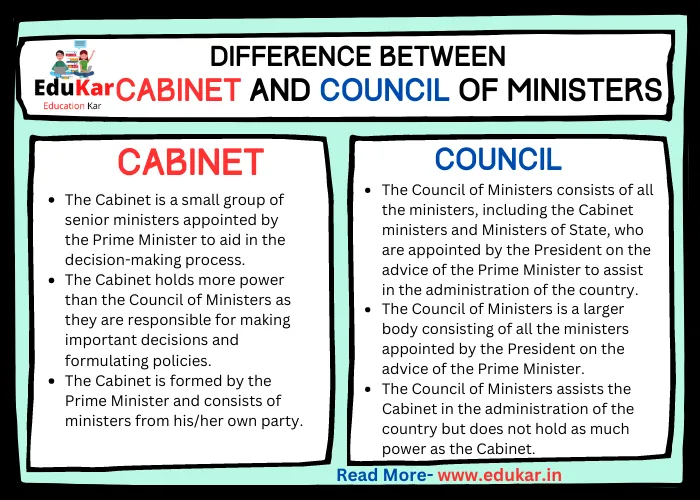
Differences between the Cabinet and Council of Ministers
| Basis of Comparison | Cabinet | Council of Ministers |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The Cabinet is a small group of senior ministers appointed by the Prime Minister to aid in the decision-making process. | The Council of Ministers consists of all the ministers, including the Cabinet ministers and Ministers of State, who are appointed by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister to assist in the administration of the country. |
| Size | The Cabinet is a smaller body consisting of a maximum of 15% of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha. | The Council of Ministers is a larger body consisting of all the ministers appointed by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister. |
| Power | The Cabinet holds more power than the Council of Ministers as they are responsible for making important decisions and formulating policies. | The Council of Ministers assists the Cabinet in the administration of the country but does not hold as much power as the Cabinet. |
| Formation | The Cabinet is formed by the Prime Minister and consists of ministers from his/her own party. | The Council of Ministers is formed by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister and consists of ministers from different political parties. |
| Meetings | The Cabinet meets regularly to discuss and make decisions on important matters. | The Council of Ministers meets less frequently than the Cabinet and mainly serves as an advisory body to the Cabinet. |
| Role | The Cabinet plays a key role in the decision-making process and is responsible for implementing the policies formulated by the government. | The Council of Ministers plays a supportive role to the Cabinet and is responsible for implementing policies in their respective departments. |
| Authority | The Cabinet holds the ultimate authority to make important decisions and approve policies. | The Council of Ministers has limited authority and mainly acts on the advice of the Cabinet. |
| Importance | The Cabinet is more important than the Council of Ministers as they are responsible for making major decisions that affect the country. | The Council of Ministers is important but not as significant as the Cabinet as they mainly assist the Cabinet in the administration of the country. |
| Appointment | Cabinet ministers are appointed by the Prime Minister and are usually senior members of his/her own party. | Ministers of State are appointed by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister and may be from any political party. |
| Resignation | A Cabinet minister may resign or be dismissed by the Prime Minister. | A Minister of State may resign or be dismissed by the Prime Minister or the President. |
Importance of understanding the difference
Understanding the difference between the Cabinet and Council of Ministers is important as it affects the governance and administration of the country. It helps to understand the structure of the Indian government and its decision-making process. It also helps to understand the role of the Prime Minister and other ministers in the government.
Also See: Difference Between Political and Permanent Executive
Summary
The Cabinet and Council of Ministers are two important bodies of the Indian government that play a crucial role in the country’s governance and decision-making process. The Cabinet is a smaller and more powerful body that takes key decisions on behalf of the government, while the Council of Ministers is advisory in nature and provides guidance and support to the Cabinet.
FAQs
What is the Cabinet?
The Cabinet is a group of senior government officials appointed by the Head of State or Government who are responsible for the overall direction and management of government policies and programs.
What is the Council of Ministers?
The Council of Ministers is a broader group of government officials that includes the Cabinet as well as other ministers or secretaries of state responsible for specific policy areas.
What is the main difference between the Cabinet and Council of Ministers?
The main difference between the Cabinet and Council of Ministers is that the Cabinet is a smaller and more influential group of senior officials who have the most authority over government decision-making, while the Council of Ministers is a larger group of officials who are responsible for implementing and executing government policies in specific areas.
Who is typically a part of the Cabinet?
The Cabinet is usually composed of senior officials such as the Prime Minister or President, Vice President, Deputy Prime Ministers, Ministers of Foreign Affairs, Finance, Defense, and other important portfolios.
Who is typically a part of the Council of Ministers?
The Council of Ministers is typically composed of all Cabinet members as well as other Ministers or Secretaries of State responsible for specific policy areas such as education, health, transportation, environment, and so on.
What are the responsibilities of the Cabinet and Council of Ministers?
The Cabinet is responsible for setting the overall direction and priorities of government policies, making major decisions on issues of national importance, and advising the Head of State or Government on key matters. The Council of Ministers is responsible for implementing and executing government policies and programs in their respective policy areas.
Can the Cabinet and Council of Ministers have overlapping responsibilities?
Yes, the responsibilities of the Cabinet and Council of Ministers can overlap in certain areas, and there may be instances where some members of the Council of Ministers have significant influence on key decisions.
Can the Cabinet and Council of Ministers be dissolved or restructured?
Yes, the Cabinet and Council of Ministers can be dissolved or restructured at the discretion of the Head of State or Government. This can happen due to changes in government priorities, political reshuffles, or other factors that may affect the composition and structure of government.