Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is the Political Executive?
- 3 What is the Permanent Executive?
- 4 Differences Between Political and Permanent Executive
- 5 Similarities Between Political and Permanent Executive
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 FAQs
- 7.1 What is the Political Executive?
- 7.2 What is the Permanent Executive?
- 7.3 What is the main difference between Political and Permanent Executive?
- 7.4 Who are the members of the Political Executive?
- 7.5 Who are the members of the Permanent Executive?
- 7.6 What are the functions of the Political Executive?
- 7.7 What are the functions of the Permanent Executive?
- 7.8 Can the Political Executive interfere in the work of the Permanent Executive?
- 7.9 Can the Permanent Executive influence the decisions of the Political Executive?
- 7.10 What is the importance of the separation of powers between Political and Permanent Executive?
Learn about the key differences between political and permanent executive roles within government systems. Discover how these two roles differ in their responsibilities, scope of power, and how they function within the larger political landscape. Gain a deeper understanding of the importance of these distinctions for effective governance and decision-making.
Introduction
The executive branch of a government is responsible for implementing and enforcing laws and policies. It comprises two major components: the Political Executive and the Permanent Executive. Both play critical roles in the functioning of a government, but they differ significantly in terms of their roles, responsibilities, and functions.
What is the Political Executive?
The Political Executive consists of elected or appointed officials who hold power for a limited period. In a parliamentary system, the Political Executive is headed by the Prime Minister or President, who is responsible for leading the government and making decisions on behalf of the country. Other members of the Political Executive may include cabinet ministers, secretaries, and advisors.
Roles and Responsibilities of the Political Executive
The Political Executive is responsible for formulating and implementing policies that align with the government’s objectives. Its responsibilities include drafting legislation, presenting budgets, managing the economy, and negotiating with foreign governments. Members of the Political Executive are accountable to the public, and their tenure is subject to elections.
Examples of Political Executive in different countries
Examples of Political Executive in different countries include the President and Cabinet members in the United States, the Prime Minister and Cabinet members in the United Kingdom, and the President and Cabinet members in France.
What is the Permanent Executive?
The Permanent Executive, on the other hand, comprises civil servants and officials who hold permanent positions in government agencies and departments. These officials are responsible for the day-to-day administration of the government and the implementation of policies and laws. The Permanent Executive is responsible for ensuring that government services are delivered efficiently, effectively, and in accordance with established procedures.
Roles and Responsibilities of the Permanent Executive
The Permanent Executive is not elected but is selected based on merit, experience, and qualifications. Members of the Permanent Executive work for the government for their entire career and are not subject to elections or political changes. They provide continuity and stability in government operations and are responsible for implementing policies regardless of the political situation.
Examples of Permanent Executive in different countries
Examples of Permanent Executive in different countries include civil servants in the United States, senior civil servants in the United Kingdom, and bureaucrats in India.
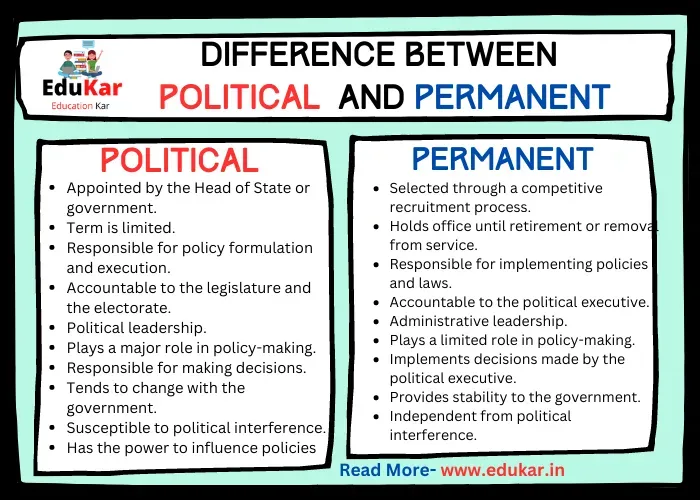
Differences Between Political and Permanent Executive
| Aspect | Political Executive | Permanent Executive |
|---|---|---|
| Appointment | Appointed by the Head of State or government | Selected through a competitive recruitment process |
| Duration | Term is limited | Holds office until retirement or removal from service |
| Responsibility | Responsible for policy formulation and execution | Responsible for implementing policies and laws |
| Accountability | Accountable to the legislature and the electorate | Accountable to the political executive |
| Role | Political leadership | Administrative leadership |
| Policy-making | Plays a major role in policy-making | Plays a limited role in policy-making |
| Decision-making | Responsible for making decisions | Implements decisions made by the political executive |
| Stability | Tends to change with the government | Provides stability to the government |
| Interference | Susceptible to political interference | Independent from political interference |
| Influence | Has the power to influence policies | Implements policies set by the political executive |
Similarities Between Political and Permanent Executive
The Political and Permanent Executive share certain similarities. Both are part of the executive branch and are responsible for implementing laws and policies. Both work towards the betterment of the country and aim to provide efficient and effective government services to citizens.
Conclusion
The Political and Permanent Executive are two important components of the executive branch of a government. While they share certain similarities, they differ significantly in terms of their roles, responsibilities, and functions. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring efficient and effective governance. By recognizing the unique strengths and limitations of each component, government officials can work together to provide the best possible services to citizens.
FAQs
What is the Political Executive?
The Political Executive is the branch of government responsible for making decisions that affect the public, such as setting policy, making laws, and enforcing regulations. It includes elected officials like the President, governors, mayors, and legislators, as well as appointed officials like cabinet members, agency heads, and judges.
What is the Permanent Executive?
The Permanent Executive is the branch of government responsible for implementing and administering the policies and laws established by the Political Executive. It includes career civil servants, such as administrators, managers, and employees of government agencies, as well as military personnel and law enforcement officials.
What is the main difference between Political and Permanent Executive?
The main difference between Political and Permanent Executive is their roles and responsibilities. The Political Executive sets policies and laws, while the Permanent Executive implements and administers those policies and laws.
Who are the members of the Political Executive?
The members of the Political Executive include elected officials like the President, governors, mayors, and legislators, as well as appointed officials like cabinet members, agency heads, and judges.
Who are the members of the Permanent Executive?
The members of the Permanent Executive include career civil servants, such as administrators, managers, and employees of government agencies, as well as military personnel and law enforcement officials.
What are the functions of the Political Executive?
The functions of the Political Executive include making policy decisions, proposing and enacting laws, appointing officials, negotiating treaties, and exercising veto power.
What are the functions of the Permanent Executive?
The functions of the Permanent Executive include implementing and administering policies and laws, managing government agencies, providing public services, and enforcing laws and regulations.
Can the Political Executive interfere in the work of the Permanent Executive?
Yes, the Political Executive can interfere in the work of the Permanent Executive to some extent. For example, the Political Executive can set policies that affect the work of government agencies, appoint officials to lead those agencies, and allocate resources to support their work.
Can the Permanent Executive influence the decisions of the Political Executive?
Yes, the Permanent Executive can influence the decisions of the Political Executive to some extent. For example, career civil servants and agency officials can provide information and expertise to elected officials, and can offer advice on the feasibility and impact of policy proposals.
What is the importance of the separation of powers between Political and Permanent Executive?
The separation of powers between Political and Permanent Executive helps to ensure that government functions effectively and remains accountable to the public. By separating policy-making from policy implementation, the government can ensure that decisions are made by elected officials who are accountable to the public, while ensuring that policies are implemented by impartial and experienced civil servants who are guided by the rule of law.