Contents
- 1 Jainism
- 2 Buddhism
- 3 Differences between Jainism and Buddhism
- 4 Conclusion
- 5 FAQs
- 5.1 What is Jainism?
- 5.2 What is Buddhism?
- 5.3 How are Jainism and Buddhism similar?
- 5.4 How are Jainism and Buddhism different?
- 5.5 Do Jainism and Buddhism share any common texts or scriptures?
- 5.6 Are there any significant differences in the way Jainism and Buddhism view the concept of karma?
- 5.7 Do Jainism and Buddhism have different practices or rituals?
- 5.8 How have Jainism and Buddhism influenced each other?
Learn about the key differences between Jainism and Buddhism, two ancient religions that originated in India. Discover their beliefs and practices, their attitudes towards karma and reincarnation, their views on the ultimate goal of life, and more. Whether you’re a curious learner or a student of comparative religion, this informative blog by Edukar will help you to understand these fascinating traditions.
Jainism and Buddhism are two ancient religions that originated in India. They share many similarities, including a focus on non-violence and self-realization. However, they also have significant differences that set them apart from each other. Understanding the differences between these two religions is essential for gaining a deeper understanding of Indian culture and history.
Jainism
Jainism is an ancient religion that originated in India around the same time as Buddhism and Hinduism. It is a spiritual path focused on the principle of Ahimsa, or non-violence, towards all living beings. This principle is at the core of Jainism, which advocates for compassion and respect for all forms of life.
Philosophy and Beliefs
Jainism is based on the idea that all living beings have a soul, and that this soul is eternal and unchanging. The goal of Jainism is to liberate the soul from the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, which is governed by the law of Karma. The Karma doctrine teaches that all actions have consequences, and that the consequences of our actions determine our future destiny.
To achieve liberation from the cycle of birth and death, Jains practice the Five Great Vows, which include non-violence, truthfulness, non-stealing, celibacy or chastity, and non-attachment. Jains also believe in the existence of three realms of existence: the heavens, the earth, and the hells. These realms are inhabited by different types of living beings, who are all subject to the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth.
Scriptures
The Jain scriptures are known as the Agamas, which are believed to be the teachings of the Tirthankaras, or enlightened beings who have attained liberation from the cycle of birth and death. The Tirthankaras are seen as spiritual guides who can help Jains on their path towards liberation.
The Jain cosmology is a complex system that describes the structure of the universe and the various realms of existence. According to Jainism, the universe is infinite and eternal, and it is divided into six parts, each with its own heavens, hells, and earths.
Practices and Rituals
Jainism is a path of self-discipline and spiritual practice. Jains practice meditation and other spiritual exercises to purify their minds and develop their spiritual awareness. Fasting and other austerities are also common practices in Jainism, as they are seen as a way to discipline the body and mind.
Jain festivals and celebrations are an important part of Jain culture. The most important festival is Mahavir Jayanti, which celebrates the birth of Lord Mahavira, the last Tirthankara of Jainism. Other important festivals include Paryushan Parva, which is a time of fasting and introspection, and Diwali, which is celebrated as the day Lord Mahavira attained enlightenment.
Buddhism
Buddhism is a major world religion that originated in ancient India and is based on the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, also known as the Buddha. Buddhism is a path of practice and spiritual development leading to insight into the true nature of reality.
Philosophy and Beliefs
The philosophy and beliefs of Buddhism can be summarized as follows:
- The Four Noble Truths:
- The Eightfold Path
- Non-self (Anatta)
- Karma
- Rebirth
- Nirvana
Scriptures
The main scriptures of Buddhism are the Tipitaka, also known as the Pali Canon, which contains the Buddha’s teachings in the form of sutras or discourses. There are also Mahayana Buddhist texts such as the Lotus Sutra and the Heart Sutra, which are highly revered by many Buddhists.
Rituals
Buddhist rituals vary depending on the tradition and country, but some common practices include meditation, chanting, offerings of food, flowers, and candles to the Buddha and other deities, and the use of prayer beads (mala). Some Buddhist traditions also have specific rituals for important occasions such as birth, marriage, and death.
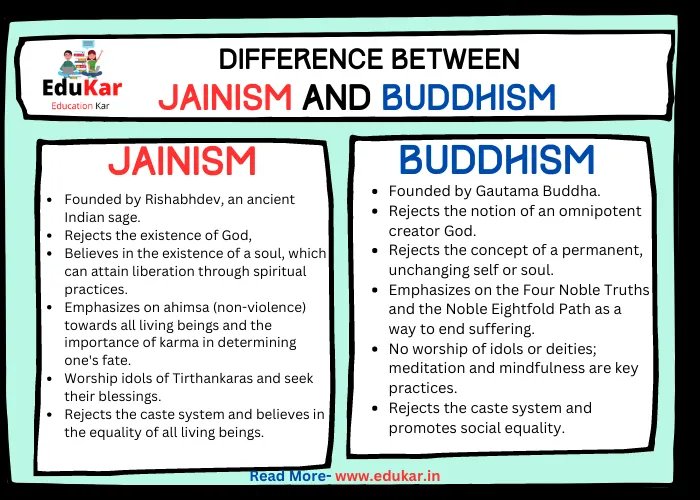
Differences between Jainism and Buddhism
| Difference | Jainism | Buddhism |
|---|---|---|
| Founder | Founded by Rishabhdev, an ancient Indian sage | Founded by Gautama Buddha |
| Belief in God | Rejects the existence of God | Rejects the notion of an omnipotent creator God |
| Concept of soul | Believes in the existence of a soul, which can attain liberation through spiritual practices | Rejects the concept of a permanent, unchanging self or soul |
| Ethics | Emphasizes on ahimsa (non-violence) towards all living beings and the importance of karma in determining one’s fate | Emphasizes on the Four Noble Truths and the Noble Eightfold Path as a way to end suffering |
| Worship | Worship idols of Tirthankaras and seek their blessings | No worship of idols or deities; meditation and mindfulness are key practices |
| Views on caste system | Rejects the caste system and believes in the equality of all living beings | Rejects the caste system and promotes social equality |
| Belief in rebirth | Believes in the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, and aims to break free from it through spiritual practices | Believes in the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, and aims to end this cycle through enlightenment |
| Dietary restrictions | Emphasizes on a vegetarian diet as a way to practice ahimsa and avoid causing harm to living beings | No specific dietary restrictions, but encourages moderation in eating and drinking |
| Views on the path to liberation | Believes in the path of right faith, right knowledge, and right conduct as a way to attain liberation | Emphasizes on the Middle Way and the Noble Eightfold Path as a way to end suffering and attain enlightenment |
| Role of the community | Emphasizes on the importance of the Jain community in practicing and promoting the principles of Jainism | Emphasizes on the individual’s responsibility to attain enlightenment and the importance of the sangha (Buddhist community) in supporting this pursuit |
Conclusion
Jainism and Buddhism share some similarities as well as significant differences. Both religions originated in ancient India and emphasize spiritual development, non-violence, and meditation. However, Jainism places greater emphasis on asceticism and the pursuit of spiritual purity, while Buddhism focuses more on the Middle Way and the development of wisdom and compassion.
Additionally, Jainism recognizes the existence of a soul or jiva, while Buddhism denies the existence of a permanent self. These differences have shaped the distinct practices, rituals, and beliefs of each religion. Jainism and Buddhism have also influenced each other over the centuries and continue to play important roles in the spiritual and cultural traditions of India and beyond.
FAQs
What is Jainism?
Jainism is an ancient Indian religion that emphasizes non-violence, self-control, and the pursuit of spiritual purity. It was founded by Mahavira in the 6th century BCE.
What is Buddhism?
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy that was founded by Siddhartha Gautama in the 5th century BCE. It emphasizes the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path as the means to attain enlightenment and escape the cycle of rebirth.
How are Jainism and Buddhism similar?
Jainism and Buddhism share some similarities, such as their origins in ancient India, their emphasis on spiritual development, and their rejection of the caste system. Both religions also teach non-violence and the importance of meditation.
How are Jainism and Buddhism different?
Jainism and Buddhism have some key differences. For example, Jainism places greater emphasis on asceticism and the pursuit of spiritual purity, while Buddhism focuses more on the Middle Way and the development of wisdom and compassion. Additionally, Jainism recognizes the existence of a soul or jiva, while Buddhism denies the existence of a permanent self.
While Jainism and Buddhism share some common themes and ideas, they do not share any common texts or scriptures. Jainism has its own canon of scriptures, known as the Jain Agamas, while Buddhism has its own canon, known as the Tripitaka.
Are there any significant differences in the way Jainism and Buddhism view the concept of karma?
Jainism and Buddhism have different views on the concept of karma. In Jainism, karma is seen as a physical substance that adheres to the soul and must be eliminated in order to achieve liberation. In Buddhism, karma is seen as a mental and moral force that creates the conditions for rebirth, but can be overcome through the cultivation of wisdom and compassion.
Do Jainism and Buddhism have different practices or rituals?
Jainism and Buddhism have different practices and rituals. Jainism emphasizes asceticism and the practice of non-violence in all aspects of life, while Buddhism places more emphasis on meditation and mindfulness. Jainism also has a complex set of dietary and behavioral rules, while Buddhism has a simpler set of ethical guidelines known as the Five Precepts.
How have Jainism and Buddhism influenced each other?
Jainism and Buddhism have had a significant influence on each other over the centuries, with ideas and practices being shared and adapted between the two religions. For example, both religions have adopted the practice of ahimsa (non-violence) and have been involved in promoting social welfare and education. However, there have also been significant differences and disagreements between the two religions, particularly regarding the nature of the self and the path to liberation.