Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Mountain
- 3 Plateau
- 4 Differences between Mountain and Plateau
- 5 Importance of Mountains and Plateaus
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 FAQs
- 7.1 What is a mountain?
- 7.2 What is a plateau?
- 7.3 How are mountains and plateaus formed?
- 7.4 What is the difference between the elevation of a mountain and a plateau?
- 7.5 What is the difference in slope between a mountain and a plateau?
- 7.6 What is the difference in topography between a mountain and a plateau?
- 7.7 Where are mountains and plateaus typically found?
Learn about the key differences between mountains and plateaus, including their formation, elevation, slope, and topography. It also discusses the ecological, economic, and cultural importance of these natural features. Learn more about the distinctions between mountains and plateaus in this informative guide.
Introduction
Mountains and plateaus are two of the most prominent geographical features on earth. They are vastly different in appearance, location, and the ecosystems they support. In this blog, we will explore the difference between mountains and plateaus, their characteristics, and the importance they hold.
Mountain
A mountain is a natural landform that rises steeply above its surrounding terrain, usually with a peak or summit.
Characteristics of Mountain
1. Height and steepness: Mountains are usually higher than their surrounding terrain and have steep sides. They are characterized by their height, and the peak or summit is usually the highest point.
2. Formation: Mountains are formed by the movements of the earth’s crust, such as tectonic plate movements or volcanic activity. Over time, the forces of erosion can shape the mountain into its unique form.
3. Location and distribution: Mountains are found all over the world, and their distribution is influenced by tectonic plate movement. The most extensive mountain ranges are found at the edges of the continents.
Examples of Famous Mountains
1. Mount Everest: Mount Everest is the highest mountain in the world, standing at 29,029 feet (8,848 meters) above sea level. It is located in the Himalayas on the border of Nepal and Tibet.
2. Kilimanjaro: Kilimanjaro is a dormant volcano in Tanzania, standing at 19,341 feet (5,895 meters) above sea level. It is the highest mountain in Africa and the highest free-standing mountain in the world.
3. Rocky Mountains: The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a vast mountain range that stretches from northern British Columbia in Canada to New Mexico in the United States.
Plateau
A plateau is a natural landform that is elevated and has a relatively flat top, steep sides, and a high elevation.
Characteristics of Plateau
1. Flat surface A plateau is characterized by its flat top, which makes it distinct from a mountain.
2. High elevation A plateau has a high elevation above sea level, making it cooler than surrounding areas.
3. Formation Plateaus are formed by the movement of tectonic plates or by the erosion of mountains over time.
Examples of Famous Plateaus
1. Tibetan Plateau: The Tibetan Plateau is the world’s highest and largest plateau, standing at an average elevation of 16,000 feet (4,900 meters) above sea level. It is located in Central Asia and covers an area of about 2.5 million square kilometers.
2. Colorado Plateau: The Colorado Plateau is a high desert region located in the southwestern United States. It covers an area of about 337,000 square kilometers and is characterized by its red sandstone cliffs and canyons.
3. Deccan Plateau: The Deccan Plateau is a large plateau located in southern India. It covers an area of about 500,000 square kilometers and is known for its volcanic formations and fertile soil.
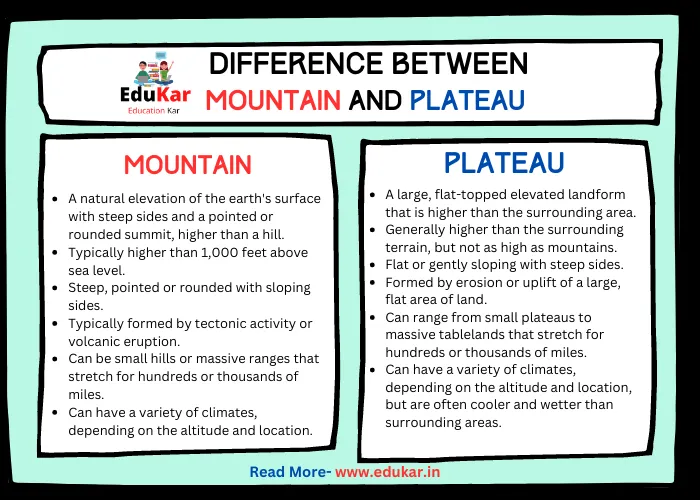
Differences between Mountain and Plateau
| Feature | Mountain | Plateau |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A natural elevation of the earth’s surface with steep sides and a pointed or rounded summit, higher than a hill | A large, flat-topped elevated landform that is higher than the surrounding area |
| Elevation | Typically higher than 1,000 feet above sea level | Generally higher than the surrounding terrain, but not as high as mountains |
| Shape | Steep, pointed or rounded with sloping sides | Flat or gently sloping with steep sides |
| Formation | Typically formed by tectonic activity or volcanic eruption | Formed by erosion or uplift of a large, flat area of land |
| Size | Can be small hills or massive ranges that stretch for hundreds or thousands of miles | Can range from small plateaus to massive tablelands that stretch for hundreds or thousands of miles |
| Climate | Can have a variety of climates, depending on the altitude and location | Can have a variety of climates, depending on the altitude and location, but are often cooler and wetter than surrounding areas |
| Vegetation | Varies based on altitude and location, but can include alpine tundra, coniferous forests, and deciduous forests | Varies based on altitude and location, but can include grasslands, savannas, and deserts |
| Human Use | Can be used for recreation, such as hiking and skiing, or for mining and logging | Often used for agriculture or grazing, but can also be used for mining and recreation |
| Examples | The Rocky Mountains, the Himalayas | The Tibetan Plateau, the Colorado Plateau |
Importance of Mountains and Plateaus
Ecological Importance
1. Habitat for wildlife: Mountains and plateaus are important habitats for a variety of plant and animal species.
2. Water resources: Mountains and plateaus are often the source of rivers and streams that provide water for human consumption and agriculture.
Economic Importance
1. Tourism: Mountains and plateaus attract millions of tourists each year, generating billions of dollars in revenue for local economies.
2. Mining: Mountains and plateaus are often rich in minerals and metals, making them important areas for mining.
Cultural Importance
1. Spiritual significance: Mountains and plateaus have long been revered by many cultures as sacred places.
2. Historical significance: Mountains and plateaus have played an important role in human history, serving as sites for important events and settlements.
Conclusion
Mountains and plateaus are two distinct geographical features with different characteristics, formations, and distributions. Mountains are characterized by their height, steep sides, peaked tops, and formation through tectonic plate movement, while plateaus have a flat top, gentle slopes, high elevation, and form through uplift or erosion.
FAQs
What is a mountain?
A mountain is a natural elevation of the earth’s surface that rises steeply to a peak or summit. It is characterized by its height, steep sides, and peaked top.
What is a plateau?
A plateau is a flat-topped natural elevation of the earth’s surface that rises above the surrounding terrain. It is characterized by its high elevation, gentle slopes, and flat top.
How are mountains and plateaus formed?
Mountains are formed by the movement of tectonic plates, while plateaus are formed by the uplift of the earth’s surface or the erosion of mountains.
What is the difference between the elevation of a mountain and a plateau?
The elevation of a mountain is typically higher than that of a plateau. Mountains can reach heights of over 20,000 feet (6,100 meters), while plateaus typically have an elevation of between 1,000 and 5,000 feet (300 and 1,500 meters) above sea level.
What is the difference in slope between a mountain and a plateau?
Mountains have steep sides, while plateaus have relatively gentle slopes that rise gradually from the surrounding terrain.
What is the difference in topography between a mountain and a plateau?
Mountains have a peaked or pointed top, while plateaus have a flat top.
Where are mountains and plateaus typically found?
Mountains are usually found in ranges or chains, while plateaus are often found as isolated highlands. They can be found in various regions around the world, including Asia, North America, South America, and Africa.