
What is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing is an industrial process of converting raw materials into some useful product for use or sale. The process is generally divided into three stages. In the first stage, raw materials are converted into intermediate products, such as semi-finished steel, pulp, and paper. In the second stage, these intermediate products are converted into further processed products, such as finished steel, paper, ketchup, or cars. In the third stage, the products are distributed to the retail and wholesale markets.
Importance of Manufacturing :-
(a) It helps in modernizing agriculture, reduce heavy dependence on agriculture by providing jobs in secondary and tertiary sector.
(b) Expert of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
(c) Industrial development is a removal of unemployement and povert from our country.
(d) Countries that transform their raw material into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and disversifying its manufacturing industries.
Contribution of Industry to National Economy :
(a) The manufacturing sector has stagnated 17% of GDP. The contribution of industry in GDP is very low in India as compared to eat asian countries.
(b) The National manufacturing competitive council (NMCC) has been set up by government to take appropriate policy measure to improve the productivity of manufacturing sector.
Factors which affect Industrial location :
(a) Raw material :- Cheap and abundant availability of raw material.
(b) Labour :- Cheap labour are necessary for low cost of production.
(c) Power :- Cheap & continuous supply of power is very must.
(d) Capital :- Necessary for entire manufacturing and for meeting manufacture expenditure.
(e) Government Policies :- There are many government policies.
Classification of Industries :
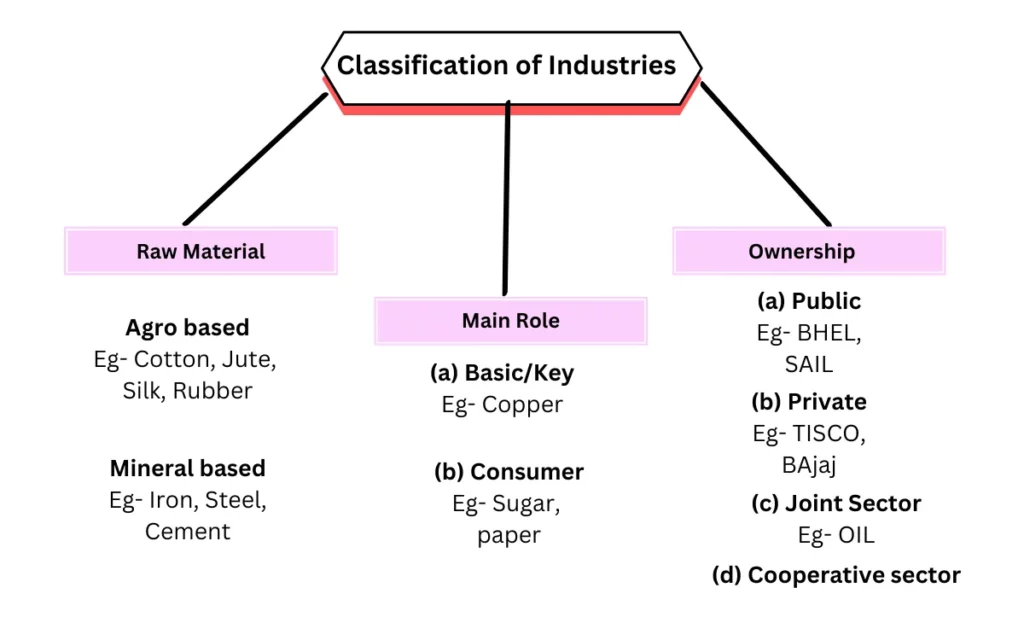
- On the basis of capital investment (a) Small scale (b) Large scale.
- On the basis of bulk and weight (a) Heavy (b) Light industry
Agro Based industries :
Agro Based industries is a company that specializes in the agricultural industry. They produce and sell agricultural products, including ingredients, and equipment. Agro Based industries helps to provide the world with a healthy and sustainable diet.
Textile industry :
The textile industry is the global industry that turns textile fibres into yarn, fabric, and finished goods. It includes manufacturing processes, textile design, and textile trade. The industry is divided into the three major types, which are cotton textile, wool textile, and silk textile.
(a) Cotton Textile Industry :-
- First cotton mill was established in 1854 in Mumbai. Cotton is produced by three method in Inida.
- Handloom – By hands.
- Powerloom – By machine
- Mills
- Generate employement for farmer and cotton ball plucker.
- Workers employed in spinning, weaving, dyeing, desugning, packaging, tailoring and seiving.
- We are having large share (1/4th) in world trade cotton yarn.
- Spinning – Concentrated in Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- Weaving – Handloom + Powerloom.
India export yarn to Japan
Imports of cotton goods :- USA, UK, Russia, Africa.
Drawbacks of Cotton Textile Industries :
- Low output of labour
- Machinery needs to be upgraded.
- Power supply is erratic (not regular)
- Stiff competition with synthetic fiber industry.
Jute Textile Industry :
Jute is a natural fiber. It is a very strong and durable material. Jute is made in many ways, including by hand and machine. This material is used to make a wide variety of products. Some are industrial, while others are consumer goods. Jute fibers are also used to make rope and twine. Jute is a versatile natural fiber.
1st Jute mill was built in Kolkata in 1859. Most mills are located in West Bengal on banks of Hugli River because of:
- Cheap labour.
- Nearby urban center (Kolkata, U.P.) that provides banking, insurance and port facilities.
- Good network of railways, roadways and waterways that make transport easy and cheap.
Challenges:
- Stiff competition from synthetic substitutes.
- International competition (Brazil & Egypt).
Sugar Industry :
Sugar is an important part of our diet. It is a vital nutrient that our body needs to function. It is important to understand how sugar affects our body in order to eat it in moderation. The sugar industry has been an important part of the food industry for hundreds of years. In the last few decades, the amount of multinational food companies has increased significantly. This has caused the sugar industry to become a type of global business.
Raw material : Bulky and it reduces sucrose content.
Location : 60% Mills are in Bihar & U.P.
Sugar Millas shifted to Southern and Western states specially Maharashtra because
- Higher sucrose content.
- Cooperative are most successful in these state.
- Cooler climate that ensure longer crushing season.
Challenges of Sugar Industry:
- Seasonal Nature
- Maximate the use of biofuel.
- Old & effecient method of production.
- Transport delay in reaching canes to factory.
Iron and Steel Industry :
The iron and steel industry is an industry that works on iron and steel. They are one of the largest industries in the world. The iron and steel industry is made up of three main types of companies. These are iron ore mines, steel mills, and steel products. This industry is known for the process of converting iron and steel into different shapes and forms.
- Heavy idustry finished goods are heavy and bulky and more transport cost.
- Iron Ore:Cooking Coal:Lime stone = 4:2:1
- Chotanagpur plateau region has maximum concentration of iron and steel industry.
- Cheap labour
- Low cost of Iron ore.
- High grade raw material.
- India is 3rd crude steel producer of Sponge Iron.
Challenges:
- Low labour productivity.
- Poor infrastucture.
- Irregular supply of power.
Aluminium Industry:
Aluminium is the main metal used to make packaging, cookware, bicycles, and many other products. As a result, aluminum is found in almost every home. Today, aluminum is used for a lot of different things, but it is also an important raw material. Aluminium is also one of the lightest metals on the planet. It is also highly resistant to corrosion and is a versatile metal. Aluminium is a sustainable metal and is recyclable.
Uses : Utensils, Wires, Aircraft.
Properties :
- Light, resistant to corrosion.
- Good conductor of heat.
- Gained popularities as a substitue of steel, copper, zinc and lead.
Location of Industry:
- Electricity power supply must be regular.
- Raw material access at low cost.
- Bauxite is the raw material used in smeters is a very bulky, dark reddish colored rock.
- Aluminium smelting plants are located in Odisha, West Bengal, Kerela & Tamil Nadu.
Fertiliser Industry
Fertiliser is a substance that enhances the growth of plants by adding nutrients to the soil. It is often sold in a liquid, powder or granular form. Fertiliser is made up of a combination of various elements that are necessary to plants. It is commonly used in commercial agriculture and is often sold in bags to be mixed with soil. Fertiliser is available in many forms and can be mixed with water and nutrients, which can then be applied to plants.
Cement Industry
Cement is a versatile and high-quality building material. It is used in construction, manufacturing, and other industries. It is made by heating a mixture of limestone and clay at high temperatures. Cement is a strong, hard, brittle and plastic building material. It is usually used with aggregate, which is a porous, aggregate material that has a particle size that is finer than sand.
Raw Material : Limestone, Silica, Aluminium, Gypsum.
- 1st plant was built in Chennai in 1904.
- Cement is mainly used at buildings, houses, factories, airports etc.
- Located in Gujarat have suitable access to the market in the Gulf countries.
Polluton due to Industries :
Air Pollution:
- Caused by Sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- Respiratory problem.
- Sources of air pollution – Chemical and paper industries, burning fossil fuels and smelting.
Water Pollution:
- Inorganic Industrial waste.
- Caused by affluents discharge.
- Sources: Paper, pulp, chemical, textile, dyeings.
- Affects aquatic life.
Thermal Pollution:
- When water from factories drained into river and ponds before there treatment.
- Sources: Nuclear plant, Weapon plant.
- Effects: Cancer, Birth defects, miscarriages.
Noise Pollution:
- Sources: Factory equipments like Generator, drills and many more.
Control of Environmental Degradation:
- Reusing and Recycling of water.
- Rainwater harvesting.
- Treating hot water before release from industries.
