Discover the key differences between Potentiometer and Voltmeter in this informative article by Edukar. Learn about the functions, uses, and advantages of each device to gain a better understanding of their unique features and applications. Whether you are an electronics enthusiast or a curious learner, this article is sure to provide you with valuable insights into these fundamental instruments.
Potentiometers and voltmeters are two electronic devices commonly used in various applications to measure electrical properties. Potentiometers and voltmeters play significant roles in electronic engineering, physics, and other technical fields that deal with electrical and electronic components. Both instruments may seem similar, but they serve different purposes, and their constructions and working principles are unique.
Potentiometer
Potentiometers are variable resistors that allow users to adjust the resistance by varying the position of the wiper on a resistive element. They have three terminals, with two outer terminals connecting to the resistive element and the third connecting to the movable wiper. Potentiometers have a wide range of applications, including volume controls on audio equipment, dimmer switches on lighting systems, and the control of robotic actuators.
Construction and Components of Potentiometer
Potentiometers come in different shapes and sizes, but their basic construction is similar. They consist of a resistive element, a wiper, and three terminals. The resistive element is typically made of a carbon composition, conductive plastic, or a wire-wound element. The wiper is a movable contact that slides along the resistive element. The three terminals are the input, output, and the wiper terminal. The input and output terminals connect to the ends of the resistive element, while the wiper terminal connects to the wiper.
Working Principle of Potentiometer
The potentiometer’s working principle is based on the relationship between the resistive element’s length and resistance. When a voltage is applied across the input and output terminals, a voltage gradient is formed across the resistive element. As the wiper is moved along the resistive element, the resistance between the wiper and the output terminal changes, altering the output voltage.
The output voltage is a fraction of the input voltage and depends on the position of the wiper along the resistive element. The resistance between the wiper and output terminal can be calculated using Ohm’s Law, where V is the voltage, R is the resistance, and I is the current flowing through the circuit.
Applications of Potentiometer
Potentiometers have a wide range of applications, including:
- Audio equipment volume controls
- Lighting systems dimmer switches
- Robotic actuators
- Thermostats
- Speed controllers
- Tuning circuits
- Balance and level controls
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used to measure the voltage difference between two points in a circuit. Voltmeters come in two types, analog and digital. Analog voltmeters use a pointer or a moving coil to indicate the voltage on a calibrated scale. Digital voltmeters convert the voltage to a digital value and display it on a screen. Voltmeters are essential tools for electrical engineers and technicians, allowing them to measure voltage accurately and troubleshoot electrical problems.
Construction and Components of Voltmeter
Voltmeters consist of a sensitive galvanometer, a resistor, and a series of switches. The galvanometer is connected in series with a resistor, forming a voltage divider circuit. The switches allow the user to select the range of the voltmeter, adjusting the resistance of the circuit to match the voltage being measured. Analog voltmeters have a scale attached to the galvanometer, while digital voltmeters display the voltage value on a screen.
Working Principle of Voltmeter
The voltmeter’s working principle is based on Ohm’s Law, which states that the current flowing through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage difference across it. When a voltage is applied to the circuit being measured, the current flows through the resistor and the galvanometer. The current flowing through the galvanometer creates a magnetic field that interacts with a permanent magnet, causing the pointer to move on an analog voltmeter or generating an electrical signal on a digital voltmeter. By selecting the proper range and measuring the current, the voltmeter can accurately measure the voltage difference between two points in a circuit.
Types of Voltmeters
There are two types of voltmeters: analog and digital. Analog voltmeters use a mechanical movement to display the voltage reading, while digital voltmeters use digital displays to show the voltage value.
Applications of Voltmeter
Voltmeters have a wide range of applications, including:
- Troubleshooting electrical circuits
- Testing batteries and power supplies
- Measuring the voltage of electronic components
- Monitoring the voltage in power distribution systems
- Testing the electrical systems in automobiles
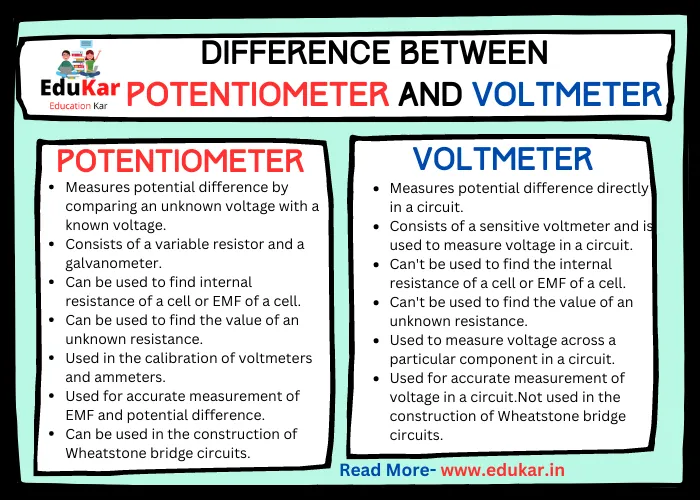
Differences between Potentiometer and Voltmeter
| Potentiometer | Voltmeter |
|---|---|
| Measures potential difference by comparing an unknown voltage with a known voltage. | Measures potential difference directly in a circuit. |
| Consists of a variable resistor and a galvanometer. | Consists of a sensitive voltmeter and is used to measure voltage in a circuit. |
| Can be used to find internal resistance of a cell or EMF of a cell. | Can’t be used to find the internal resistance of a cell or EMF of a cell. |
| Can be used to find the value of an unknown resistance. | Can’t be used to find the value of an unknown resistance. |
| Used in the calibration of voltmeters and ammeters. | Used to measure voltage across a particular component in a circuit. |
| Used for accurate measurement of EMF and potential difference. | Used for accurate measurement of voltage in a circuit. |
| Can be used in the construction of Wheatstone bridge circuits. | Not used in the construction of Wheatstone bridge circuits. |
| Has a variable resistance which can be adjusted to get the desired voltage. | Has a fixed resistance and measures voltage across a component. |
| Has a high internal resistance compared to voltmeters. | Has a low internal resistance compared to potentiometers. |
| Used in the calibration of pH meters, thermocouples and thermometers. | Not used in the calibration of pH meters, thermocouples and thermometers. |
Summary
Potentiometers and voltmeters are two essential electronic instruments used to measure electrical properties. Potentiometers are variable resistors used to vary the resistance in a circuit, while voltmeters are used to measure the voltage difference between two points in a circuit. Despite having some similarities, such as the use of resistive elements, their constructions and working principles are different. Understanding the differences between potentiometers and voltmeters is essential for anyone working with electronic components and circuits.
FAQs
What is a potentiometer?
A potentiometer is an instrument that measures the potential difference or voltage between two points in a circuit. It consists of a resistive element and a sliding contact, or wiper, that moves along the element to vary the voltage.
What is a voltmeter?
A voltmeter is an instrument that measures the voltage or potential difference between two points in a circuit. It is typically used to measure the voltage across a specific component or part of a circuit.
What is the difference between a potentiometer and a voltmeter?
The main difference between a potentiometer and a voltmeter is that a potentiometer is used to vary the voltage in a circuit, while a voltmeter is used to measure the voltage or potential difference between two points in a circuit. In other words, a potentiometer is a variable resistor, while a voltmeter is a measuring instrument.
How does a potentiometer work?
A potentiometer works by varying the voltage across a resistive element. As the sliding contact or wiper moves along the resistive element, the voltage at the output terminal of the potentiometer changes, allowing for a variable voltage output.
How does a voltmeter work?
A voltmeter works by connecting in parallel with the component or part of a circuit that needs to be measured. It measures the voltage drop across the component or part and displays the result on a meter.
When should I use a potentiometer?
A potentiometer is typically used in situations where the voltage needs to be varied or adjusted, such as in audio equipment, lighting systems, and electronic circuits.
When should I use a voltmeter?
A voltmeter is typically used in situations where the voltage or potential difference between two points in a circuit needs to be measured, such as in troubleshooting electrical problems or measuring the performance of a specific component or part of a circuit.
Can a potentiometer be used as a voltmeter?
No, a potentiometer cannot be used as a voltmeter. While both instruments measure voltage, a potentiometer is a variable resistor that can change the voltage output, while a voltmeter is a measuring instrument that only measures the voltage or potential difference between two points in a circuit.
Can a voltmeter be used as a potentiometer?
No, a voltmeter cannot be used as a potentiometer. While both instruments measure voltage, a voltmeter is a measuring instrument that only measures the voltage or potential difference between two points in a circuit, while a potentiometer is a variable resistor that can change the voltage output.