Learn about the key differences between Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis, the processes by which male and female reproductive cells are produced in plants. Discover where these processes occur in a flower, the number and size of cells produced, and their significance in plant breeding.
Introduction
Plants reproduce sexually through the process of gametogenesis. In angiosperms, gametogenesis occurs in the flowers. The male gametes or pollen grains are produced by microsporogenesis, whereas the female gametes or embryo sacs are produced by megasporogenesis.
Microsporogenesis
Microsporogenesis is the process of the formation of microspores, which give rise to pollen grains. It occurs in the anthers of the flower. The anthers are the male reproductive parts of the flower that produce pollen grains. Microsporogenesis involves meiosis, which is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. The following are the stages of microsporogenesis:
Prophase I: Chromosomes condense, and homologous chromosomes pair up.
Metaphase I: The homologous pairs line up in the center of the cell.
Anaphase I: Homologous pairs separate and move to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase I: The cell divides, resulting in two haploid cells.
Meiosis II: Each of the two haploid cells divides again to form four haploid microspores.
The significance of microsporogenesis is that it results in the production of pollen grains that are essential for sexual reproduction in plants.
Megasporogenesis
Megasporogenesis is the process of the formation of megaspores, which give rise to embryo sacs. It occurs in the ovules of the flower. The ovules are the female reproductive parts of the flower that produce embryo sacs. Megasporogenesis also involves meiosis. The following are the stages of megasporogenesis:
Megaspore mother cell formation: A single cell in the ovule undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid cells, out of which only one survives and forms the megaspore mother cell.
Megaspore mother cell division: The megaspore mother cell divides mitotically to form a linear structure of cells, which is the embryo sac.
Development of megaspores: One of the cells in the embryo sac develops into the functional megaspore.
Formation of embryo sacs: The functional megaspore undergoes three rounds of mitotic division to form an eight-nucleate embryo sac.
The significance of megasporogenesis is that it results in the production of embryo sacs that contain the female gametes, which are necessary for sexual reproduction in plants.
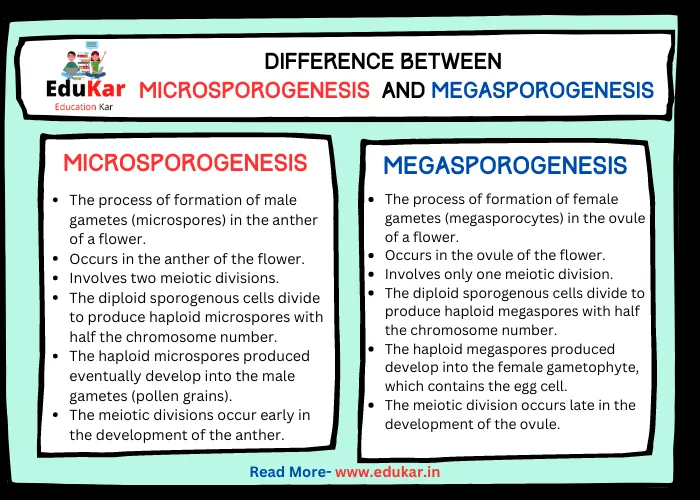
Difference between Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis
| Difference | Microsporogenesis | Megasporogenesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of formation of male gametes (microspores) in the anther of a flower | The process of formation of female gametes (megasporocytes) in the ovule of a flower |
| Occurrence | Occurs in the anther of the flower | Occurs in the ovule of the flower |
| Number of divisions | Involves two meiotic divisions | Involves only one meiotic division |
| Chromosome number | The diploid sporogenous cells divide to produce haploid microspores with half the chromosome number | The diploid sporogenous cells divide to produce haploid megaspores with half the chromosome number |
| Production of gametes | The haploid microspores produced eventually develop into the male gametes (pollen grains) | The haploid megaspores produced develop into the female gametophyte, which contains the egg cell |
| Timing of meiosis | The meiotic divisions occur early in the development of the anther | The meiotic division occurs late in the development of the ovule |
| Location of gametes | The male gametes are produced outside the ovule, and must travel to the ovule for fertilization | The female gametes are produced inside the ovule |
| Fertilization | The male gametes fertilize the female gametes to produce the zygote | The female gametes are fertilized by the male gametes to produce the zygote |
| Genetic variability | The meiotic divisions and subsequent processes lead to genetic variability in the offspring | The genetic variability is lower as there is only one meiotic division |
| Importance | Essential for sexual reproduction and for crop production through hybridization | Essential for sexual reproduction and for crop production through hybridization |
Difference between Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis in points:
1. Definition: Microsporogenesis is the process of formation of microspores, which are the male gametophytes of plants. Megasporogenesis is the process of formation of megaspores, which are the female gametophytes of plants.
2. Occurrence: Microsporogenesis occurs in the anthers of the flower, whereas Megasporogenesis occurs in the ovules of the flower.
3. Timing: Microsporogenesis takes place earlier than Megasporogenesis, typically during the tetrad stage in meiosis. Megasporogenesis usually occurs later in the life cycle of the plant.
4. Ploidy level: Microsporogenesis produces microspores that are haploid, meaning they have a single set of chromosomes. Megasporogenesis produces megaspores that are also haploid.
5. Number of spores produced: Microsporogenesis produces a large number of microspores, typically ranging from hundreds to thousands. Megasporogenesis produces a relatively smaller number of megaspores, usually four in number.
6. Fate of spores: Microspores develop into male gametophytes (pollen grains) through the process of microgametogenesis. Megaspores, on the other hand, develop into female gametophytes (embryo sacs) through the process of megagametogenesis.
7. Cell division: Microsporogenesis involves two rounds of meiotic division, resulting in the formation of four haploid microspores. Megasporogenesis involves only one round of meiotic division, resulting in the formation of four haploid megaspores.
8. Significance: Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis are important processes in plant reproduction. They result in the formation of male and female gametophytes, respectively, which are essential for sexual reproduction in plants.
Conclusion
Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis are two important processes in the reproduction of plants. While they share some similarities, such as producing haploid spores, they differ in their timing, location, and number of spores produced. Microsporogenesis occurs earlier than Megasporogenesis and produces a larger number of spores. Megasporogenesis, on the other hand, produces fewer spores but they are larger in size. The development of these spores into male and female gametophytes is crucial for sexual reproduction in plants. Understanding the differences between these two processes is important for plant breeders and geneticists in order to manipulate and control plant reproduction.
FAQs
What is Microsporogenesis?
Microsporogenesis is the process of formation and development of microspores, which are the male reproductive cells produced in the anthers of a flower.
What is Megasporogenesis?
Megasporogenesis is the process of formation and development of megaspores, which are the female reproductive cells produced in the ovules of a flower.
What is the main difference between Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis?
The main difference between Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis is the type of reproductive cell produced. Microsporogenesis produces male reproductive cells, while Megasporogenesis produces female reproductive cells.
Where do Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis occur in a flower?
Microsporogenesis occurs in the anthers of a flower, while Megasporogenesis occurs in the ovules of a flower.
What is the role of Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis in sexual reproduction?
Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis are both essential for sexual reproduction in plants. The male and female reproductive cells produced by these processes combine during fertilization to form a zygote, which eventually develops into a new plant.
What is the difference in the number of reproductive cells produced in Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis?
Microsporogenesis typically produces numerous microspores, while Megasporogenesis usually produces only a few megaspores.
How do the products of Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis differ in terms of size?
Microspores are generally smaller in size than megaspores.
What is the ploidy level of the reproductive cells produced in Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis?
The reproductive cells produced in Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis are haploid, meaning they contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
What is the significance of Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis in plant breeding?
Microsporogenesis and Megasporogenesis are important in plant breeding as they allow for the production of new plant varieties with desired traits through controlled pollination and hybridization.