Looking to understand the differences between a heat pump and a refrigerator? This article by Edukar explains how both systems operate, their key components, and the distinct functions they serve.
Introduction
Heat pumps and refrigerators are two devices that operate on similar principles but are designed for different purposes. Both devices transfer heat from one place to another using a refrigerant, which is a chemical substance that is circulated in a closed loop.
Heat Pumps
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat from one location to another using a refrigerant. The refrigerant absorbs heat from a low-temperature source and releases it at a higher temperature. Heat pumps can be used for both heating and cooling, making them versatile systems for residential and commercial applications. There are three types of heat pumps: air source, ground source, and water source.
Also Read: Difference Between 3-star and 5-star AC
Types of Heat Pumps
1. Air Source Heat Pumps: Air source heat pumps (ASHPs) extract heat from the outside air and transfer it inside a building to provide warmth. ASHPs are the most common type of heat pump and are relatively easy to install. They are ideal for moderate climates with temperatures ranging from 25°F to 55°F. ASHPs have two main components: an outdoor unit and an indoor unit. The outdoor unit contains the compressor and the heat exchanger, while the indoor unit consists of the air handler and the evaporator.
2. Ground Source Heat Pumps: Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs), also known as geothermal heat pumps, extract heat from the ground and transfer it to a building. GSHPs are highly efficient and can save up to 50% on heating and cooling costs compared to conventional systems. They are ideal for colder climates where temperatures can drop below 25°F. GSHPs have two main components: a ground loop and a heat pump unit. The ground loop is buried in the ground and contains a mixture of water and antifreeze. The heat pump unit contains the compressor, the heat exchanger, and the refrigerant.
3. Water Source Heat Pumps: Water source heat pumps (WSHPs) extract heat from a water source, such as a lake, river, or well, and transfer it to a building. WSHPs are highly efficient and can save up to 40% on heating and cooling costs compared to conventional systems. They are ideal for areas with a large body of water or a high groundwater table. WSHPs have two main components: a water loop and a heat pump unit. The water loop circulates water through the heat exchanger, which absorbs or releases heat, depending on the mode of operation.
Benefits of Using Heat Pumps
Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps are highly efficient and can save up to 50% on energy costs compared to conventional heating and cooling systems. They are also environmentally friendly, as they use less energy and emit fewer greenhouse gases.
1. Versatility: Heat pumps can be used for both heating and cooling, making them versatile systems for residential and commercial applications. They can also be used for water heating and pool heating.
2. Cost Savings: Although the initial cost of a heat pump may be higher than a conventional system, the long-term cost savings on energy bills can make up for the investment.
3. Comfort: Heat pumps provide consistent and even heating and cooling, creating a comfortable indoor environment.
Examples of Heat Pump Applications
1. Residential Heating and Cooling: Heat pumps can be used in residential buildings to provide heating and cooling. ASHPs are commonly used in moderate climates, while GSHPs are used in colder climates.
2. Commercial Heating and Cooling: Heat pumps can be used in commercial buildings to provide heating and cooling. WSHPs are commonly used in commercial buildings with a large body of water or a high groundwater table.
3. Water Heating: Heat pumps can be used to heat water for domestic use, such as showering and washing dishes.
Refrigerators
A refrigerator is a device used for food preservation. It operates on the same principle as a heat pump, but in reverse. A refrigerator transfers heat from the inside of the unit to the outside to keep food cold. There are three main types of refrigerators: standard, side-by-side, and French door.
Types of Refrigerators
1. Standard Refrigerators: Standard refrigerators have a single door and a freezer compartment located either on the top or bottom. They are the most common type of refrigerator and are available in various sizes and configurations.
2. Side-by-Side Refrigerators: Side-by-side refrigerators have two doors that open vertically. The refrigerator compartment is on one side, and the freezer compartment is on the other. They are ideal for small kitchens or households that require more freezer space.
3. French Door Refrigerators: French door refrigerators have two doors that open horizontally, with the refrigerator compartment on top and the freezer compartment on the bottom. They are popular for their large capacity and easy access to food.
Also Read: Difference Between Si and Ci Engines
Benefits of Using Refrigerators
1. Food Preservation: Refrigerators are essential for food preservation, as they keep food fresh and prevent spoilage.
2. Convenience: Refrigerators provide a convenient storage solution for food and beverages, allowing for easy access and organization.
3. Energy Efficiency: Refrigerators are becoming more energy-efficient, reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
Examples of Refrigerator Applications
1. Residential Use: Refrigerators are used in residential homes to store food and beverages.
2. Commercial Use: Refrigerators are used in commercial establishments, such as restaurants and grocery stores, to store and display food and beverages.
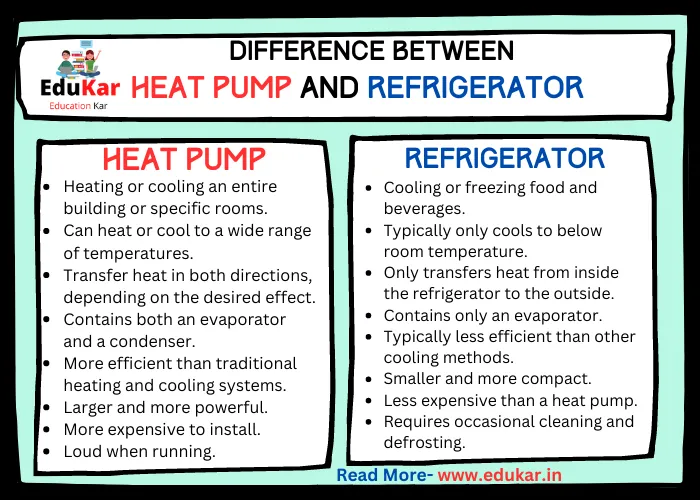
Differences between Heat Pumps and Refrigerators
| Heat Pump | Refrigerator | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Heating or cooling an entire building or specific rooms | Cooling or freezing food and beverages |
| Temperature range | Can heat or cool to a wide range of temperatures | Typically only cools to below room temperature |
| Direction of heat transfer | Transfer heat in both directions, depending on the desired effect | Only transfers heat from inside the refrigerator to the outside |
| Components | Contains both an evaporator and a condenser | Contains only an evaporator |
| Energy efficiency | More efficient than traditional heating and cooling systems | Typically less efficient than other cooling methods |
| Size | Larger and more powerful | Smaller and more compact |
| Noise | Loud when running | Generally runs quietly |
| Cost | More expensive to install | Less expensive than a heat pump |
| Environment | Eco-friendly heating and cooling option | Contribute to food waste if not used efficiently |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance to ensure proper functioning | Requires occasional cleaning and defrosting |
Summary
Both heat pumps and refrigerators operate on the same thermodynamic principles, but their applications and design differ.
Heat pumps are designed to transfer heat from one location to another, often to heat a space or water. Refrigerators are designed to remove heat from a confined space to cool and preserve food or other perishable items.
While both devices use similar technology, the design and application of each differ significantly. Understanding these differences is important for selecting the appropriate device for a given application and ensuring efficient and effective use of energy.
Ultimately, heat pumps and refrigerators are both crucial in our daily lives and play vital roles in maintaining our comfort, convenience, and health.
Also Read: Difference Between IoT and M2M
FAQs
What is a heat pump?
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat from one location to another using electricity or fossil fuels. It can be used to heat or cool spaces, and can also be used to heat water.
What is a refrigerator?
A refrigerator is a device that uses electricity to remove heat from the confined space inside the unit, which cools the items stored in it and preserves their freshness.
What is the main difference between a heat pump and a refrigerator?
Both heat pumps and refrigerators use similar thermodynamic principles to transfer heat, the main difference is their application and design. Heat pumps are designed to transfer heat from one location to another, often to heat a space or water, while refrigerators are designed to remove heat from a confined space to cool and preserve food or other perishable items.
Can a heat pump be used as a refrigerator?
Yes, a heat pump can be used as a refrigerator by reversing the direction of the refrigerant flow.
Can a refrigerator be used as a heat pump?
Yes, a refrigerator can be used as a heat pump by reversing the direction of the refrigerant flow. However, this is not very efficient and is not commonly used.
Which is more energy-efficient, a heat pump or a refrigerator?
It depends on the application. Heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient than electric heaters or boilers for heating a space or water, but refrigerators are designed to be highly efficient for cooling and preserving food.
Can a heat pump be used in colder climates?
Yes, heat pumps can be used in colder climates, but some models may require a backup heating system to operate efficiently in very low temperatures.
How long do heat pumps and refrigerators typically last?
The lifespan of a heat pump or refrigerator depends on factors such as usage, maintenance, and quality of construction. Generally, a well-maintained heat pump or refrigerator can last 10 to 20 years or more.