This article explains the difference between Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat, which are two important institutions of local self-government in rural areas of India. It also covers the roles and responsibilities of each institution, the challenges they face, and how these challenges can be overcome.
Introduction
India is a vast country with a diverse population, and local governance plays a vital role in the effective delivery of services and resources. Gram Sabhas and Gram Panchayats are two important institutions of local governance in India. While both of these institutions are essential in local governance, they differ in composition, membership, functions, and responsibilities.
Gram Sabha
Gram Sabhas are village-level assemblies that function as a direct democracy forum for the people. The term “Gram Sabha” literally translates to “Village Assembly.” The primary purpose of the Gram Sabha is to discuss and decide on issues related to the development of the village. The Gram Sabha is composed of all the adults of the village who are registered as voters. This means that every person who is 18 years of age or older and has their name on the voter list is a member of the Gram Sabha.
The Gram Sabha meets at least twice a year and discusses various issues such as water, sanitation, health, education, and agriculture. The Gram Sabha is responsible for identifying and prioritizing the developmental needs of the village and ensuring that the Gram Panchayat works to meet those needs.
Gram Panchayat
Gram Panchayats are elected bodies that are responsible for the implementation of various developmental schemes in the village. The term “Gram Panchayat” translates to “Village Council.” The Gram Panchayat is composed of elected representatives from the village. The number of members in the Gram Panchayat depends on the population of the village. The Gram Panchayat is responsible for planning and executing various developmental schemes in the village such as building roads, schools, and hospitals. It is also responsible for the maintenance of various public assets such as community centers, public parks, and water sources.
The Gram Panchayat works under the guidance of the Gram Sabha. The Gram Sabha has the power to approve the annual plans of the Gram Panchayat and to monitor the implementation of these plans. The Gram Sabha also has the power to approve the annual budget of the Gram Panchayat.
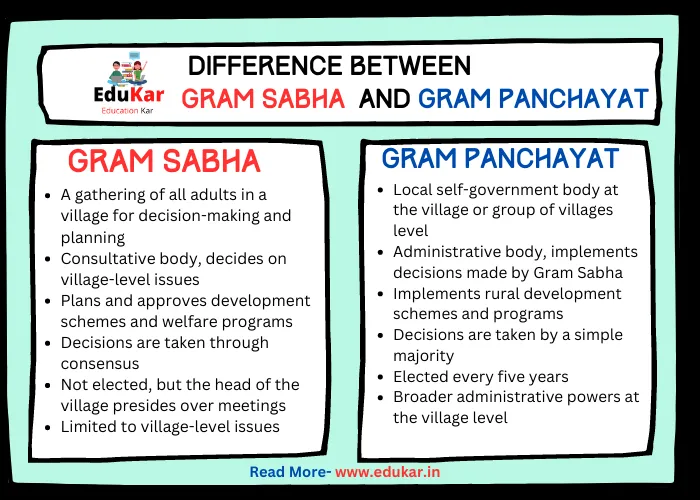
| Criteria | Gram Sabha | Gram Panchayat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A gathering of all adults in a village for decision-making and planning | Local self-government body at the village or group of villages level |
| Membership | All adults in the village | Elected members (Sarpanch, Ward Members) |
| Role | Consultative body, decides on village-level issues | Administrative body, implements decisions made by Gram Sabha |
| Function | Plans and approves development schemes and welfare programs | Implements rural development schemes and programs |
| Meetings | At least twice a year | Monthly or as required |
| Decision-making | Decisions are taken through consensus | Decisions are taken by a simple majority |
| Election | Not elected, but the head of the village presides over meetings | Elected every five years |
| Funds | No direct access to funds, but can recommend schemes to the Gram Panchayat | Direct access to funds and has the power to approve budgets |
| Accountability | Not accountable for implementation of schemes | Accountable for implementation of schemes |
| Disputes | Can mediate disputes between villagers | Can resolve disputes between residents |
| Role in governance | Primary democratic institution at the village level | Basic unit of local self-government |
| Decision-making power | Limited to village-level issues | Broader administrative powers at the village level |
| Control | Gram Sabha exercises control over Gram Panchayat | Gram Panchayat exercises control over village-level administration |
Issues and challenges in the functioning of Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat
While Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat are important institutions of local self-government in rural areas of India, they face several issues and challenges in their functioning. Some of the major issues and challenges are as follows:
1. Low Participation
One of the significant challenges faced by Gram Sabha is low participation by its members. In many villages, people are not aware of the importance of Gram Sabha, and hence, they do not attend the meetings.
2. Lack of Resources
Gram Panchayats face the problem of lack of resources, which makes it difficult for them to carry out their responsibilities effectively. The funds provided by the government are often insufficient to meet the needs of the village.
3. Political Interference
Another issue faced by Gram Panchayats is political interference. The local politicians often interfere in the functioning of Gram Panchayats, which affects their decision-making process.
4. Lack of Expertise
The members of Gram Panchayats often lack the required expertise to carry out their responsibilities effectively. They may not have the necessary knowledge or skills to implement development programs in the village.
5. Corruption
Corruption is a major challenge faced by Gram Panchayats. The funds meant for development programs may be siphoned off by corrupt officials or contractors, which affects the implementation of programs.
6. Caste and Gender Discrimination
In many villages, caste and gender discrimination affect the functioning of Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat. Women and people from lower castes may not have equal representation or may face discrimination in decision-making.
To overcome these issues and challenges, there is a need to create awareness among people about the importance of Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat. The government should also provide adequate resources and training to the members of Gram Panchayats to enable them to carry out their responsibilities effectively. Measures should be taken to prevent political interference and corruption, and steps should be taken to ensure equal representation and participation of women and people from lower castes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat are two distinct entities in the Indian rural governance system. Gram Sabha is the assembly of all adult members of a village, while Gram Panchayat is the elected body that governs the village. Gram Sabha serves as a platform for local decision-making, whereas Gram Panchayat is responsible for implementing these decisions and managing the village’s administrative affairs. Although Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat work together in promoting rural development, their functions and roles are different, and it’s important to understand the distinction between them to effectively participate in rural governance. Overall, both these institutions play a critical role in the empowerment of rural communities and the strengthening of India’s grassroots democracy.
FAQs related to Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat for Exams:
What is Gram Sabha?
Gram Sabha is a general assembly of all the adult members of a village or a group of villages who have the right to participate in the decision-making process of the village.
What is Gram Panchayat?
Gram Panchayat is a local self-government body at the village level that is responsible for implementing the policies and programs of the government related to rural development.
What is the difference between Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat?
Gram Sabha is a general assembly of all the adult members of a village, while Gram Panchayat is a local self-government body responsible for implementing the policies and programs related to rural development.
Who heads the Gram Panchayat?
The Gram Panchayat is headed by a Sarpanch, who is elected by the members of the Gram Sabha
What is the role of Gram Sabha in the functioning of Gram Panchayat?
Gram Sabha elects the members of the Gram Panchayat and approves its plans and budgets. It also has the right to review the performance of the Gram Panchayat and provide feedback.
What are the responsibilities of Gram Panchayat?
The Gram Panchayat is responsible for providing basic amenities such as water supply, sanitation, health, education, and infrastructure in the village. It is also responsible for implementing government policies and programs related to rural development.
What are the challenges faced by Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat?
The challenges faced by Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat include low participation, lack of resources, political interference, lack of expertise, corruption, and caste and gender discrimination.
How can these challenges be overcome?
These challenges can be overcome by creating awareness among people about the importance of Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat, providing adequate resources and training to the members of Gram Panchayats, preventing political interference and corruption, and ensuring equal representation and participation of women and people from lower castes.