Looking to understand the difference between delegation and decentralization? This comprehensive guide explores the key differences between these two management concepts, including their respective advantages and disadvantages. Discover how delegation and decentralization can impact your organization’s structure, decision-making processes, and overall effectiveness.
Delegation
Definition of delegation
Delegation is the process of assigning tasks or responsibilities to another person, while still retaining ultimate responsibility for the outcome.
Examples of delegation in the workplace
Delegation can take many forms in the workplace, such as assigning a project to a team member, delegating administrative tasks to an assistant, or assigning a task to a consultant or contractor.
Benefits of delegation
Delegation can help to distribute workload, empower team members, and allow for greater efficiency and productivity.
Challenges of delegation
Delegation can be challenging, as it requires trust in team members, clear communication, and the ability to provide feedback and support as needed.
Decentralization
Definition of decentralization
Decentralization is the process of distributing decision-making power and authority across different levels of an organization.
Examples of decentralization in the workplace
Decentralization can take many forms in the workplace, such as giving teams the authority to make decisions about their work, empowering local branches or offices to make decisions independently, or allowing individual employees to make decisions about their own work.
Benefits of decentralization
Decentralization can help to promote innovation, reduce bureaucracy, and allow for greater responsiveness to local needs and conditions.
Challenges of decentralization
Decentralization can be challenging, as it requires clear communication, coordination, and the ability to balance local autonomy with organizational goals and priorities.
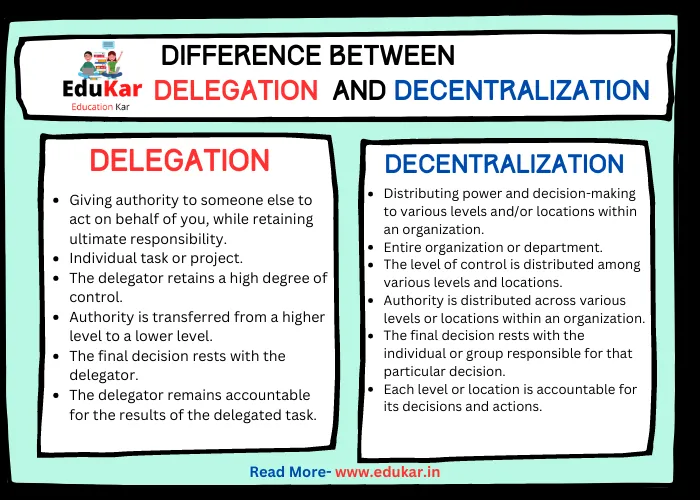
Differences between Delegation and Decentralization
| Difference | Delegation | Decentralization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Giving authority to someone else to act on behalf of you, while retaining ultimate responsibility | Distributing power and decision-making to various levels and/or locations within an organization |
| Focus | Individual task or project | Entire organization or department |
| Degree of control | The delegator retains a high degree of control | The level of control is distributed among various levels and locations |
| Level of authority | Authority is transferred from a higher level to a lower level | Authority is distributed across various levels or locations within an organization |
| Decision-making | The final decision rests with the delegator | The final decision rests with the individual or group responsible for that particular decision |
| Accountability | The delegator remains accountable for the results of the delegated task | Each level or location is accountable for its decisions and actions |
| Scope | Limited in scope and time | Broader in scope and more permanent |
| Flexibility | Less flexible as the delegator may need to be consulted for certain decisions | More flexible as decision-making is distributed to various levels and locations |
| Communication | Communication is more hierarchical as decisions are made by the delegator and passed down | Communication is more lateral as decision-making is distributed across various levels and locations |
| Outcome | More focused on achieving specific goals and objectives | More focused on adapting to changing circumstances and achieving overall organizational goals |
Conclusion
Delegation and decentralization are two related but distinct concepts that can be used to distribute responsibility and authority in the workplace.Understanding the differences between delegation and decentralization can help leaders and managers to make more informed decisions about how to structure their teams and organizations, and how to distribute responsibility and authority for the best outcomes.
FAQs
How do delegation and decentralization differ?
Delegation and decentralization differ in terms of the degree of control retained by the person or organization delegating or decentralizing. Delegation involves assigning tasks or responsibilities while retaining ultimate responsibility for the outcome, while decentralization involves distributing decision-making power and authority across different levels of an organization.
What are the benefits of delegation?
Delegation can help to distribute workload, empower team members, and allow for greater efficiency and productivity.
What are the challenges of delegation?
Delegation can be challenging, as it requires trust in team members, clear communication, and the ability to provide feedback and support as needed.
What are the benefits of decentralization?
Decentralization can help to promote innovation, reduce bureaucracy, and allow for greater responsiveness to local needs and conditions.
What are the challenges of decentralization?
Decentralization can be challenging, as it requires clear communication, coordination, and the ability to balance local autonomy with organizational goals and priorities.
When should I use delegation?
Delegation can be more efficient and effective in situations where there is a clear hierarchy and decision-making structure.
When should I use decentralization?
Decentralization can be more effective in situations where there is a need for innovation and responsiveness to local conditions.
How do I decide between delegation and decentralization?
Factors to consider when deciding between delegation and decentralization could include the size and structure of the organization, the nature of the task or decision, the degree of expertise and experience required, and the level of risk involved.




