Discover the key differences between biogas and natural gas in this informative article by Edukar. Learn about the advantages and limitations of each energy source, their chemical composition and properties, and how they compare in terms of cost, availability, and environmental impact.
Introduction
Energy is a vital component of modern life, and there are many sources of energy available today, from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. Biogas and natural gas are two types of gas that are often compared, and it is important to understand the differences between them. Biogas is a renewable energy source that is produced from the breakdown of organic matter, while natural gas is a non-renewable fossil fuel that is formed from the decay of ancient organisms.
Biogas
Biogas is a renewable energy source that is produced from the breakdown of organic matter. It is typically produced through a process called anaerobic digestion, which involves the decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. The sources of biogas can include animal manure, agricultural waste, and municipal waste.
Also See: Difference between Meristematic Tissue and Permanent Tissue
Chemical Composition and Properties of Biogas
Biogas is primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), with small amounts of other gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and water vapor (H2O). The exact composition of biogas depends on the source of the organic matter used in its production.
Advantages of Using Biogas
There are several advantages to using biogas as an energy source.
- Biogas is a renewable energy source, meaning that it can be produced indefinitely as long as there is a supply of organic matter.
- Biogas production reduces greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere.
- Biogas can be a cost-effective energy source, particularly in rural areas where there is an abundance of organic waste.
Limitations and Challenges of Biogas
Despite its advantages, biogas also has limitations and challenges.
- The production of biogas requires specialized equipment and expertise, which can be expensive.
- Biogas has a low energy density compared to other fuels, which means that large quantities of biogas are required to generate the same amount of energy as other fuels.
- Biogas typically has a high moisture content, which can make storage and transportation difficult.
Natural Gas
Natural gas is a fossil fuel that is formed from the decay of ancient organisms over millions of years. It is typically found in underground reservoirs, and is extracted through drilling.
Chemical Composition and Properties of Natural Gas
Natural gas is primarily composed of methane (CH4), with small amounts of other gases such as ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and butane (C4H10). The exact composition of natural gas depends on the source of the gas.
Advantages of Using Natural Gas
There are several advantages to using natural gas as an energy source.
- Natural gas is a clean-burning fuel that produces fewer emissions than other fossil fuels.
- Natural gas is widely available and is used for a variety of purposes, including heating and electricity generation.
- Natural gas has a high energy density, meaning that it produces a lot of energy per unit of volume.
Limitations and Challenges of Natural Gas
Despite its advantages, natural gas also has limitations and challenges.
- Natural gas is a non-renewable resource, meaning that it will eventually run out.
- The extraction and use of natural gas can contribute to climate change through the release of greenhouse gases such as methane.
- Natural gas can be prone to leaks, which can have safety and environmental implications.
Also See: Difference between Binary Fission and Multiple Fission
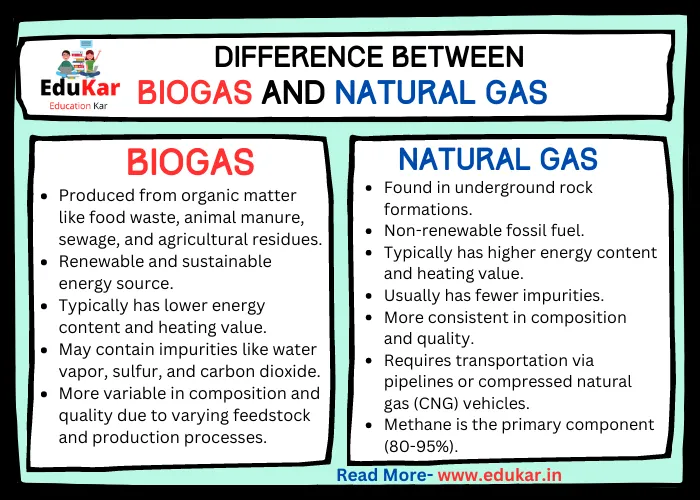
Differences between Biogas and Natural Gas
| S.No. | Biogas | Natural Gas |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Produced from organic matter like food waste, animal manure, sewage, and agricultural residues | Found in underground rock formations |
| 2. | Renewable and sustainable energy source | Non-renewable fossil fuel |
| 3. | Typically has lower energy content and heating value | Typically has higher energy content and heating value |
| 4. | May contain impurities like water vapor, sulfur, and carbon dioxide | Usually has fewer impurities |
| 5. | Carbon neutral as it doesn’t add new carbon to the atmosphere | Contributes to carbon emissions when burned |
| 6. | More variable in composition and quality due to varying feedstock and production processes | More consistent in composition and quality |
| 7. | Methane is the primary component (50-70%) | Methane is the primary component (80-95%) |
| 8. | Can be produced on-site, reducing transportation costs and emissions | Requires transportation via pipelines or compressed natural gas (CNG) vehicles |
| 9. | Requires specific equipment and infrastructure for production and use | Widely available infrastructure for production and use |
| 10. | Can be used for heat and electricity generation, as well as vehicle fuel | Primarily used for heat and electricity generation, but also as a vehicle fuel |
Also See: Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell
Summary
In conclusion, while biogas and natural gas share some similarities in their chemical composition and properties, they are fundamentally different sources of energy. Biogas is a renewable energy source that is produced from organic matter through a process called anaerobic digestion, while natural gas is a non-renewable fossil fuel that is formed from the decay of ancient organisms.
Both energy sources have their advantages and limitations, and choosing between them depends on a variety of factors such as cost, availability, and environmental impact. Ultimately, it is important to continue exploring and developing renewable energy sources like biogas, in order to reduce our reliance on non-renewable sources of energy like natural gas and reduce the impact of climate change.
FAQs
What is biogas?
Biogas is a renewable energy source that is produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter such as agricultural waste, sewage, and food waste.
What is natural gas?
Natural gas is a fossil fuel that is formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals. It is primarily composed of methane and is extracted from underground reservoirs.
How are biogas and natural gas different?
Biogas and natural gas differ in their sources, composition, and environmental impacts. Biogas is derived from organic waste and is a renewable energy source, while natural gas is a non-renewable fossil fuel. Biogas typically contains a higher percentage of carbon dioxide than natural gas and can also contain trace amounts of impurities such as hydrogen sulfide. Natural gas, on the other hand, is primarily composed of methane and may contain small amounts of other gases such as ethane and propane.
Can biogas be used in the same way as natural gas?
Yes, biogas can be used in many of the same applications as natural gas, including heating, cooking, and generating electricity. However, biogas may need to be processed and purified before it can be used in certain applications.
Which is more environmentally friendly, biogas or natural gas?
Biogas is generally considered to be more environmentally friendly than natural gas because it is a renewable energy source and has a lower carbon footprint. Biogas is produced from waste materials that would otherwise be disposed of in landfills or released into the atmosphere, while natural gas is a finite resource that requires energy-intensive extraction methods.
Is biogas more expensive than natural gas?
The cost of biogas and natural gas can vary depending on a variety of factors, including the availability and proximity of the resources, the processing required, and local market conditions. In some cases, biogas may be more expensive than natural gas due to higher production and processing costs. However, biogas may also be eligible for government subsidies or tax credits that can make it more cost-competitive with natural gas.
Can biogas and natural gas be used together?
Yes, biogas and natural gas can be blended together and used as a fuel source. This can help to increase the availability of renewable energy while also reducing the carbon footprint of natural gas. However, biogas and natural gas have different characteristics and may require different equipment and processing methods to be blended effectively.